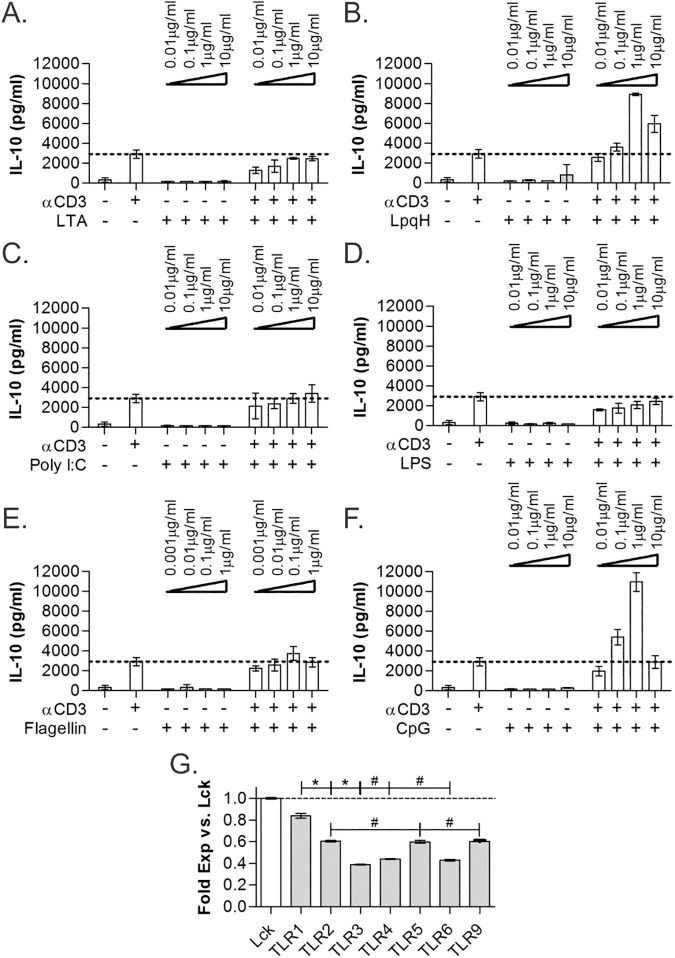
Fig 4. TLR2 and TLR9 show similar IL-10-induction activity.
Co-stimulation of WT CD4+ T cells, isolated using MACS, with different TLR agonists at varying concentrations was performed for 3 days and IL-10 quantified by ELISA. The TLR2/6-dependent agonist lipoteichoic acid (LTA) failed to increase IL-10 (A), whereas the TLR2/1-dependent LpqH (B) and P3C (see Fig 1) showed IL-10 synergy. Similar to LTA, TLR3-dependent Poly I:C (C), TLR4-dependent LPS (D), and TLR5-dependent flagellin (E) all failed to increase IL-10. As seen with P3C and LpqH, the TLR9-dependent CpG also induced robust IL-10 synergy (F). mRNA transcript levels of the TLR genes from freshly isolated unstimulated WT CD4+ T cells was measured by microarray. Normalized expression levels compared to the canonical T cell marker Lck (G) are shown. TLR1, expressed at essentially the same level as Lck, is the most highly expressed TLR gene. All data are n≥3, unless otherwise noted; only LpqH and CpG showed significant increases in IL-10 over baseline (p<0.05); *p<0.05; #p>0.05.