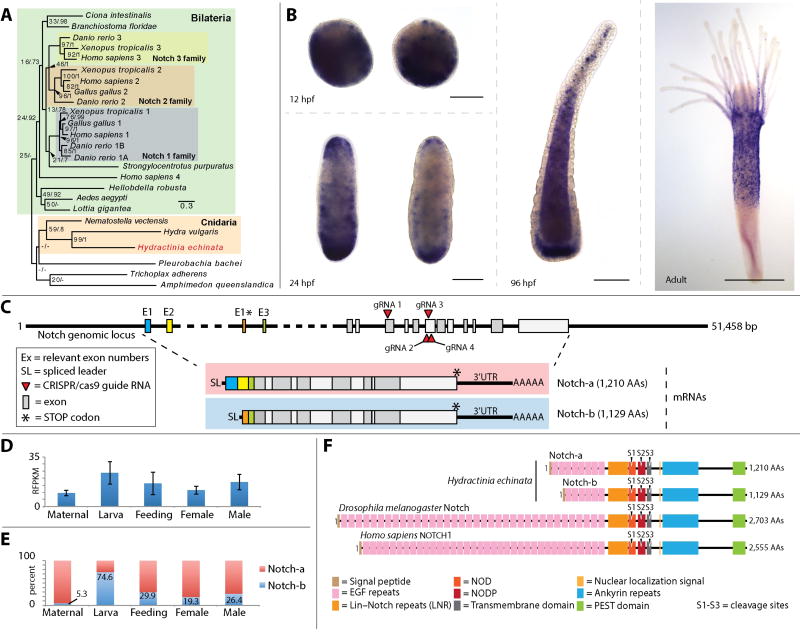
Figure 1. Notch phylogeny, expression, genomic architecture and alternative splicing.
(A) Unrooted maximum likelihood/Baysian phylogeny of Hydractinia echinata Notch; scale bar = nucleotide changes per site. (B) In-situ hybridization showing Notch mRNA expression patterns at 12, 24 and 96 hours post fertilization (hpf), and adult polyp; scale bar = 100 µm in embryos and larva, and 300 µm in the polyp. (C) Notch genomic locus showing CRISPR-Cas9 guide RNA sites, alternative exons and the complete architecture of the mRNA for the two notch isoforms. (D) Notch expression levels in Hydractinia eggs (maternal transcripts), larvae, feeding, and male and female polyps. (E) Ratio of expression of Notch isoforms in percent across the same life stages shown in (D). (F) Domain structure of Notch isoform 1 and isoform 2 alongside Drosophila Notch and Human Notch1.