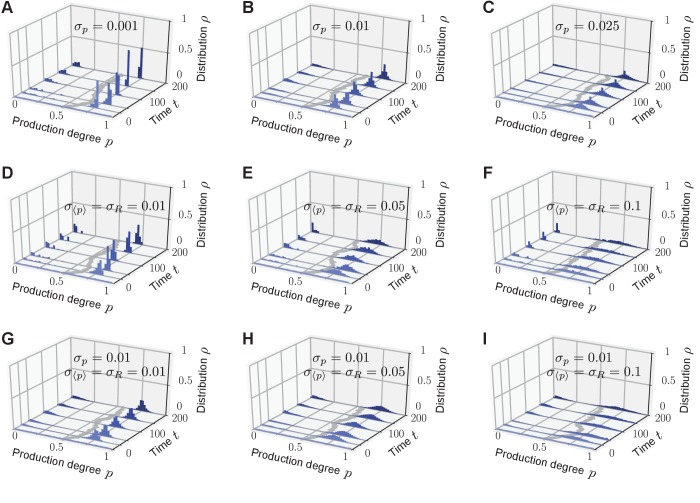
Appendix 1—figure 2. Phenotypic heterogeneity in the quorum-sensing model is robust against noisy inheritance, noisy perception, and noisy response.
Upon including either noisy inheritance of the production degree (A–C), or noisy perception of the average production level and noisy response to it (D–F), or both percx="">(G-I) into the model set-up, bimodal quasi-stationary states still arise in the relevant parameter regimes (see Figure 2C). Depicted are representative single realizations of the modified stochastic process (histogram over normalized values of production degrees to make the comparison with Figure 2 possible). (A–C) Noisy inheritance is implemented at reproduction events. Production degree is passed on to an offspring as with noise sampled from a Normal distribution (and are cut off such that ), emulating noisy inheritance of the phenotype. characterizes the strength of the noise ( recovers noiseless inheritance). As increases, bimodal quasi-stationary states still arise, but the two peaks become broader than in the noiseless case. (D–F) Noise in the sensing apparatus is implemented as noisy perception of the average production level with Gaussian noise , and noise in the response is implemented at the level of the response function as with Gaussian noise . Therefore, the production degree of an individual is updated through sense-and-response to the environment as in the quorum-sensing model. Again, as the strength of both sense and response noise increase, bimodal quasi-stationary states still arise, but the two peaks become broadened compared with the noiseless case. We emphasize that corresponds to very strong noise on the interval . (G–I) Combined effect of noisy inheritance and noisy sense-and-response. Representative trajectories demonstrate that bimodal quasi-stationary states also arise in the presence of noise at all update steps. Thus, phenotypic heterogeneity in the quorum-sensing model is qualitatively robust against noise at all steps. Initial distribution: , independent and identically distributed; Parameters: selection strength , response probability , response function , and population size .