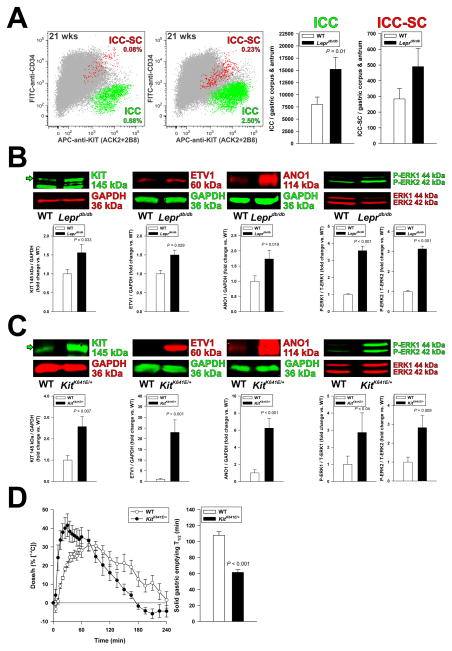
Figure 2.
Increased ICCs contribute to accelerated gastric emptying. (A) Increased ICC (KIT+CD34− cells; green) and ICC-SC (KITlowCD34+cells; red) numbers detected by FCM in the non-hematopoietic, CD44+ fraction (gray) of gastric muscles of Leprdb/db mice vs. WT controls (n=9/group). (B) Expression of the key ICC proteins KIT, ETV1, and ANO1 and ERK1-ERK2 phosphorylation (WB; n=4–15/group) were significantly increased in Leprdb/db mice. (C–D) ICC hyperplasia associates with accelerated gastric emptying of solids in KitK641E/+ mice. (C) Consistent with the ICC hyperplasia previously reported in this strain,5 KIT, ETV1 and ANO1 expression and ERK1-ERK2 phosphorylation were elevated by WB in gastric corpus+antrum tunica muscularis tissues of female KitK641E/+ mice vs. controls (n=8–12/group). (D) Time course (left) and half-times (T1/2; right) of solid gastric emptying measured by [13C]-octanoic acid breath test in female KitK641E/+ mice (n=5–6/group). Note rapid emptying in the KitK641E/+ animals. Green arrows in B and C indicate mature, 145-kDa KIT protein.