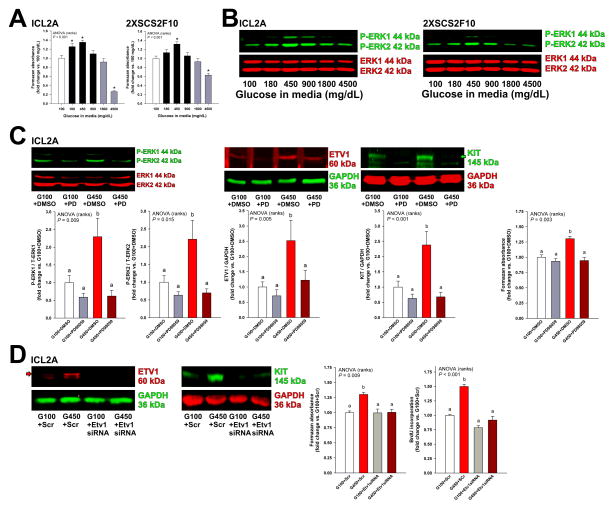
Figure 5.
Hyperglycemia stimulates the growth of ICC and ICC-SC cell lines via the ERK-ETV1-KIT pathway. (A–B) Effect of high glucose on cell counts determined by MTS assay (A; n=3–9/cell line/group) and ERK1-ERK2 phosphorylation analyzed by WB (B; n=6/cell line/group) in ICL2A and 2XSCS2F10 cells. Cell numbers and ERK1-ERK2 phosphorylation were significantly increased by high glucose levels typically seen in Leprdb/db mice (*, P<0.05 vs. 100 mg/dL glucose) and were only reduced by extremely high concentrations. (C) In ICL2A cells, the MAPK kinase inhibitor PD98059 (PD; 20 μM) inhibited hyperglycemia-induced ERK1-ERK2 phosphorylation and upregulation of ETV1 and KIT proteins (n=8–12/group) and cell counts (n=6/group). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide vehicle. G100 and G450, 100 and 450 mg/dL glucose, respectively. (D) siRNA-mediated knock-down of ETV1 inhibited the hyperglycemia-induced increase in ETV1 and KIT protein levels (WB), cell numbers (MTS) and proliferation (BrdU incorporation) detected in ICL2A cells (n=6/group). Scr, scrambled-sequence control. Green and red arrows indicate mature, 145-kDa KIT and 60-kDa ETV1 proteins, respectively. Groups in B and D not sharing the same superscript are different by post-hoc tests (P<0.05).