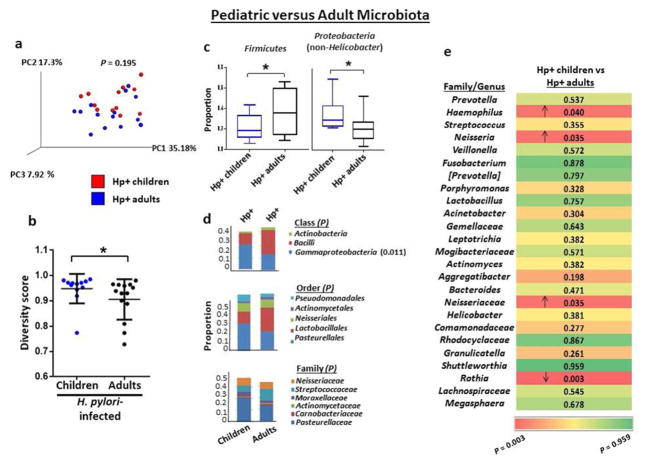
Figure 4.
The gastric microbiota in H. pylori-infected children differs from that of infected adults. (a) PCoA plot of the gastric microbiota of H. pylori-infected children (n=12) and infected adults (n=14) with weighted Unifrac as the distance measure. P value was determined using the permanova test in QIIME. (b) Richness and abundance distribution of the gastric microbiota in children and adults with H. pylori infection. Alpha diversity was determined using the Simpson index, and horizontal lines indicate mean ±standard deviation (SD). (c) The proportions of Firmicutes and non-Helicobacter Proteobacteria were significantly different in the stomachs of H. pylori-infected children and infected adults. Box-and-whisker plots display the median, maximum and minimum values for the indicated group. (d) Frequencies of gastric bacteria by class, order and family in H. pylori-infected children and infected adults. Analysis was performed as described in Figure 2b. (e) Gastric microbiota by genera in H. pylori-infected children and infected adults. Analysis was performed as described in Figure 2c. *P<0.05, Student’s t-test (b) or the Kruskal Wallis test (c).