Figure 5. Intestinal helminth infection results in the systemic and sustained redistribution of the naive lymphocyte pool.
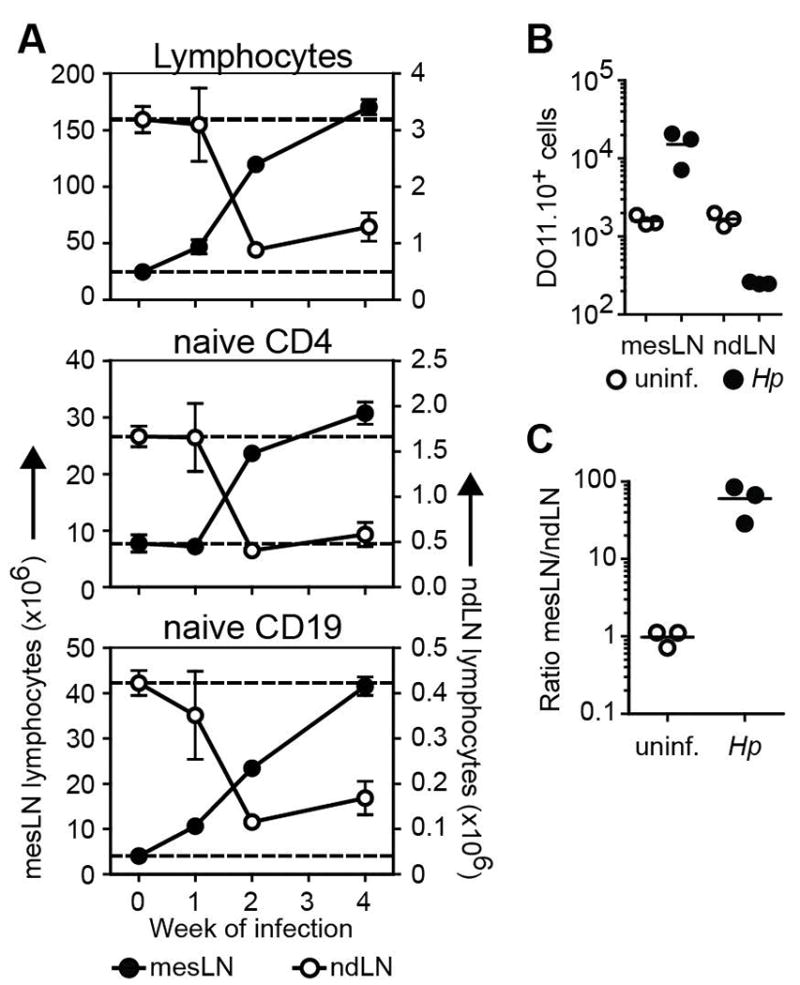
(A) BALB/c or 4get BALB/c mice were infected with Hp and the number of total lymphocytes and naive phenotype CD4+ T and CD19+ B cells in the mesLN (left Y axis) and the pooled non-draining inguinal, axillary and brachial LN (ndLN) (right Y axis) were determined at the indicated time points. Each data point shows the mean of 3-5 individual mice and error bars indicate the SEM. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. (B) OVA-specific CD4+ T cells from Thy1.2+ DO11.10 mice were transferred into uninfected or day 11 Hp infected Thy1.1+ congenic mice. The number of Thy1.2+KJ1-26+ donor CD4+ T cells in the mesLN or the pooled non-draining inguinal, axillary and brachial LN (ndLN) was determined one hour later by flow cytometry. (C) The relative recruitment of DO11.10 donor cells into the mesLN relative to the ndLN was calculated based on the total numbers determined in B. Scatter plots in B and C show data from individual mice. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 3 mice per group.
