Figure 6. Intestinal helminth compromises immunity to heterologous challenge at peripheral sites.
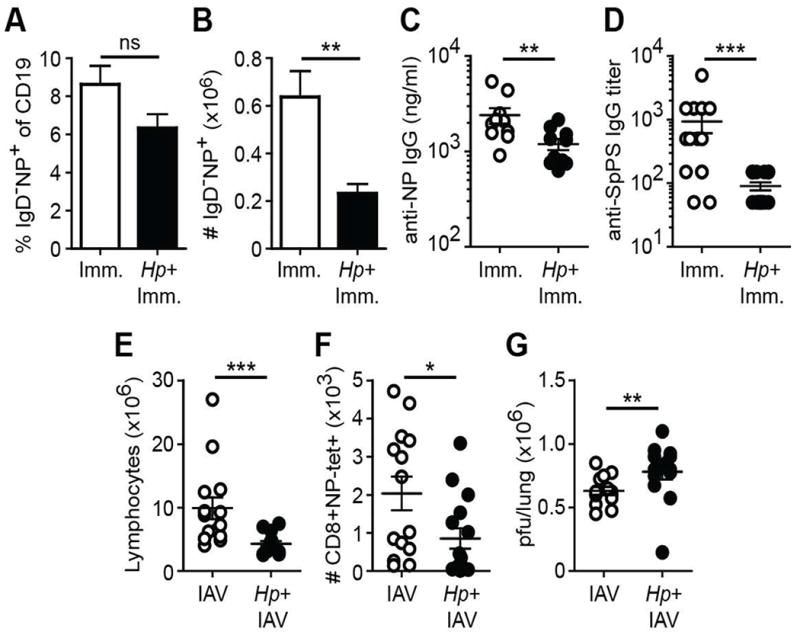
C57BL/6 mice were infected with Hp or remained naive. Two weeks later the animals were heterologously challenged. (A-C) One week after footpad immunization with NP-KLH in alum, the frequency (A) and number (B) of IgD- isotype switched NP-specific B cells in the draining popliteal LNs were determined by flow cytometry. (C) Serum anti-NP IgG titers at day 21 after NP-KLH immunization. (D) Hp-infected or naïve mice were immunized i.m. with the anti-pneumococcal vaccine formulation Prevnar13® and anti-S. pneumoniae polysaccharide IgG titers were determined 4-5 weeks later. (E, F) Number of total (E) or influenza (IAV)-specific CD8+ effector T lymphocytes (F) from the mediastinal LN of Hp-infected or helminth-naïve animals 7 days after i.n. infection with 50 pfu IAV. (G) Pulmonary viral load (pfu) was determined at day 7 post-IAV infection. Data shown is pooled from two independent experiments containing a total of 14-15 mice/group. Error bars indicate the SEM. ns, not significant; *p < .05, **p < .01 ***p < .001.
