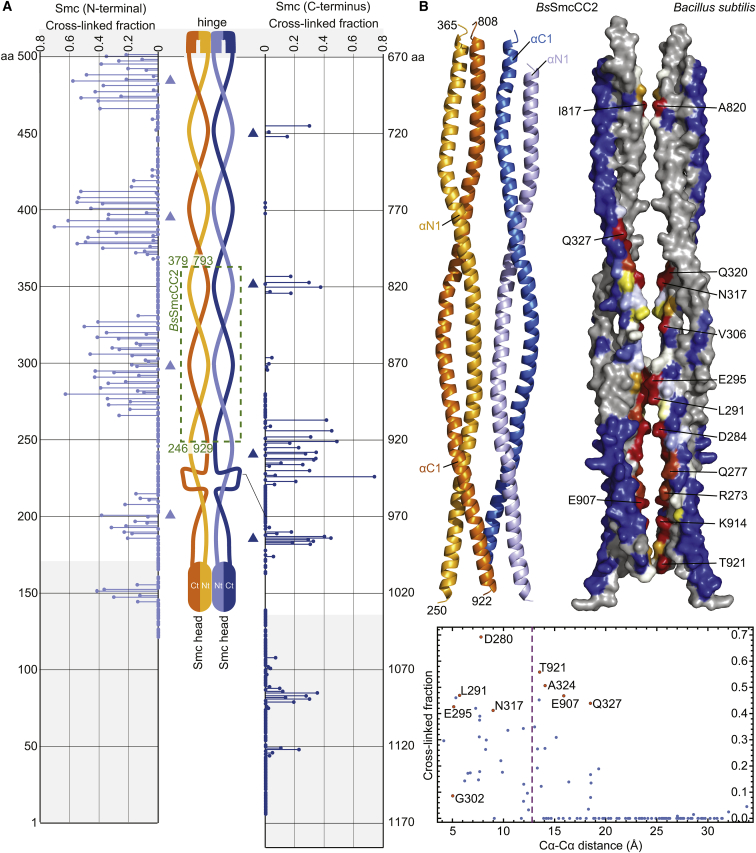
Figure 2.
Mapping of the Smc Rod by Cysteine Cross-Linking and Structural Analysis
(A) HTP cysteine cross-linking. Schematic representation of the bacterial Smc homodimer (middle). Cross-linking efficiency is given as fraction of cross-linked to total Smc-HaloTag species. For N- and C-terminal Smc(Cys) residues, the data points are displayed on the left and right graphs in light and dark blue colors, respectively. Head and hinge regions are indicated by gray shading. Triangles in light and dark blue colors denote interfaces at N- and C-terminal Smc regions, respectively. A table with corresponding cross-linking efficiencies is available (Table S4).
(B) The structure of a middle segment of the Bs Smc rod reveals the longitudinal alignment of the Smc coiled coils. Cartoon representation of the structure of the BsSmcCC2 dimer in side view (left). Monomers are displayed in orange and blue colors, respectively. Mapping of in vivo cross-linking efficiency onto BsSmcCC2 in surface representation (right). Residues are color coded according to the cross-linking efficiency given in (A): blue, yellow, orange, and red colors indicate no, low, medium, and high cross-linking efficiency, respectively. Residues colored in gray have not been tested. The identity of selected residues with medium and high cross-link efficiency is denoted. A graph displaying the cross-linking efficiency (from A) relative to the distance of respective Cα atoms in the BsSmcCC2 structure is shown (bottom). For selected residues, data points are denoted and labeled in orange colors. A dashed line indicates the linker length of BMOE plus the length of two cysteine side chains.