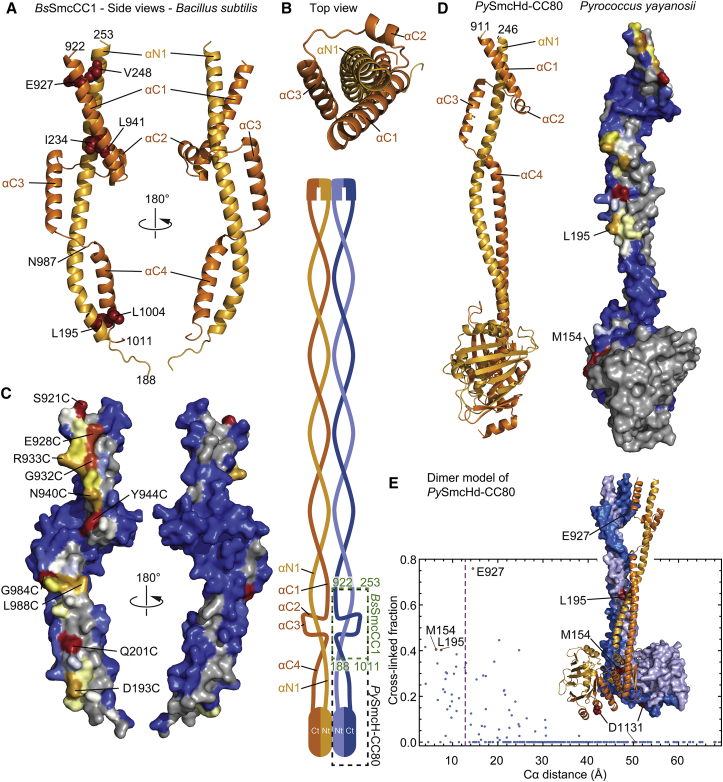
Figure 3.
The Organization of the Head-Proximal Smc Joint
(A) Structure of BsSmcCC1. Display and color coding as in Figure 2B. Front and back view are shown on the left and right, respectively.
(B) Top view of BsSmcCC1. As in (A).
(C) Mapping of the in vivo cross-linking efficiency onto BsSmcCC1. Surface representation of structural views shown in (A). Color coding as in Figure 2B.
(D) Crystal structure of PySmcHd-CC80 shown in cartoon and surface representation on the left and right, respectively. Color coding as in Figure 2B. Mapping of the Bs Smc cross-linking efficiencies onto PySmcHd-CC80 based on sequence alignments shown in Figure S4D. Please note that all cross-linking competent residues are arranged in a line on the surface of the molecule.
(E) Model of a PySmcHd-CC80 dimer. Two copies of PySmcHd-CC80 were aligned manually by minimizing the distance between cross-linking residues, thereby producing a tight dimer with little or no steric clashes. Monomers are displayed in cartoon and surface representation. Color coding as in Figure 2B. The graph displays the cross-linking efficiency of Bs Smc(Cys) residues given in Figure 2A versus the Cα-Cα distance of corresponding residues in the dimer model of PySmcHd-CC80.