Figure 5.
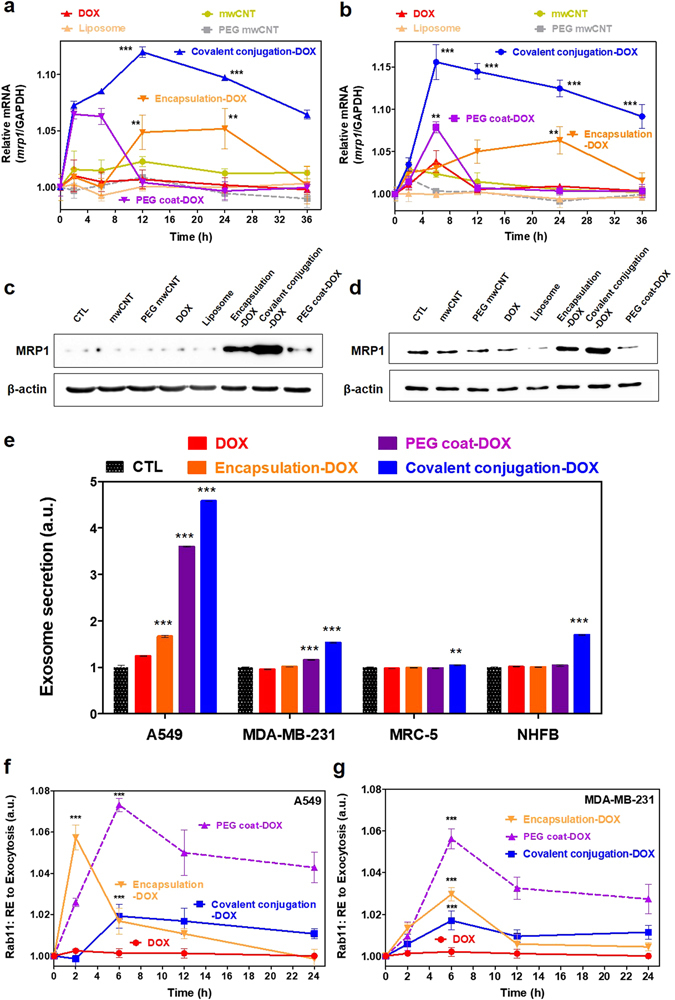
Extracellular pathway (efflux, exosomes and RE exocytosis) of nanodrugs. Time-dependent cellular removal of nanodrugs by efflux pumps (mrp-1) in (a) A549 and (b) MDA-MB-231 cells. Although PEG coat, liposomal encapsulation and free drugs exhibited relatively short time periods of efflux upregulation, covalent conjugation (blue line) exhibited prolonged upregulation (i.e., approximately 36 hrs) of the cancer efflux system (mrp-1 gene expression). Western blot analysis of MRP-1 expression after treatment (24 hrs) of nanodrugs in (c) A549 and (d) MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. (e) Secreted exosomes from cancer cells (e.g., A549 and MDA-MB-231) and normal cells (e.g., MRC-5 and NHFB) showed significant in nanodrug samples with covalent conjugation (blue) compared to liposomal encapsulation (orange) and free DOX (red) after 24 hrs. Time dependent analysis of Rab11 expression (indicative of RE to exocytosis). PEG coated conjugation (i.e., DOX: purple marker) exhibited increased Rab11 levels compared to covalent conjugation (blue) and liposomal encapsulation (orange) in (f) A549 and (g) MDA-MB-231 cell lines. Efflux and exosome data represents the mean ± SEM (n = 3). RE exocytosis data represents the mean ± SEM (n = 5). *, ** and *** correspond to p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively, as compared with free DOX (i.e., red).
