Figure 4.
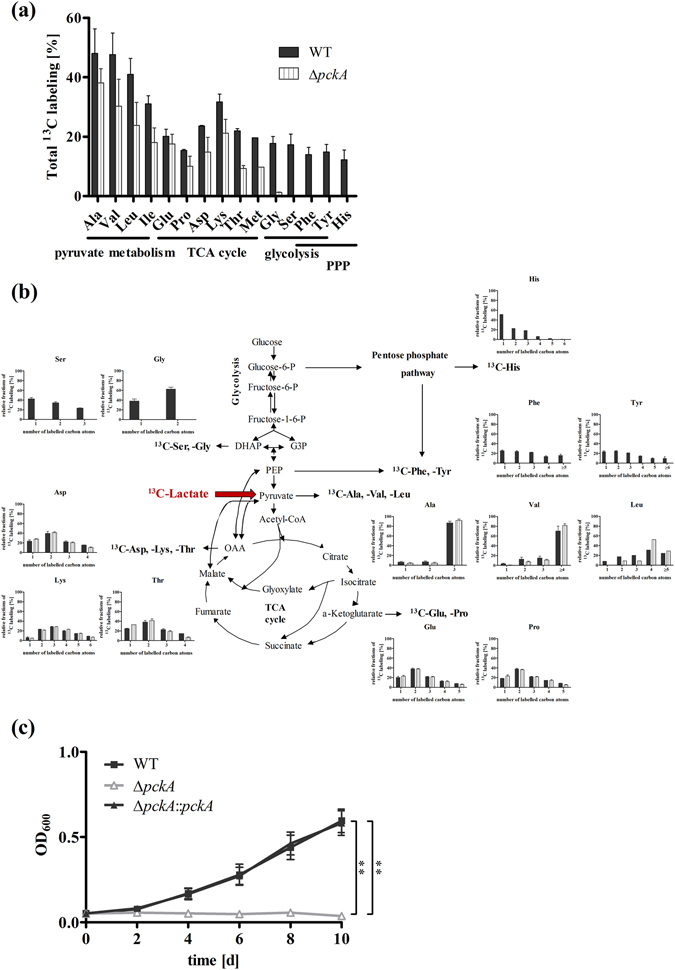
Comparison of lactate derived 13C-carbon flux in Mtb wild type and the ∆pckA mutant with a defect in gluconeogenesis, and growth of the ∆pckA mutant on lactate. To characterize the lactate derived carbon flux in Mtb, the Mtb Erdman wild type strain (black bars) and the ∆pckA mutant (striped bars) were grown for two days in medium containing 10 mM glucose and 10 mM [U-13C3]-L-lactate. Labelling patterns in amino acids were detected by GC/MS analysis. The overall 13C-enrichments are depicted in (a). The relative fractions (%, y-axis) of 13C-labelled isotopologues of the wild type strain (black bars) and the ∆pckA mutant (striped bars) with a given number of 13C-atoms (x-axis) are shown in (b). Data represent the mean of two independent experiments each measured in technical triplicates; error bars indicate the SEM. (c) To determine the impact of phosphoenolpyruvate decarboxykinase (PckA) activity on lactate utilization, growth of Mtb Erdman wild-type (black squares), the ∆pckA mutant (grey triangles) and the complemented strain (black triangles) was measured for 10 days in the presence of L-lactate as sole carbon substrate. The influence of impaired gluconeogenesis on growth was measured via optical density at the indicated time points. Data represent the mean of three independent experiments; error bars indicate the SEM.
