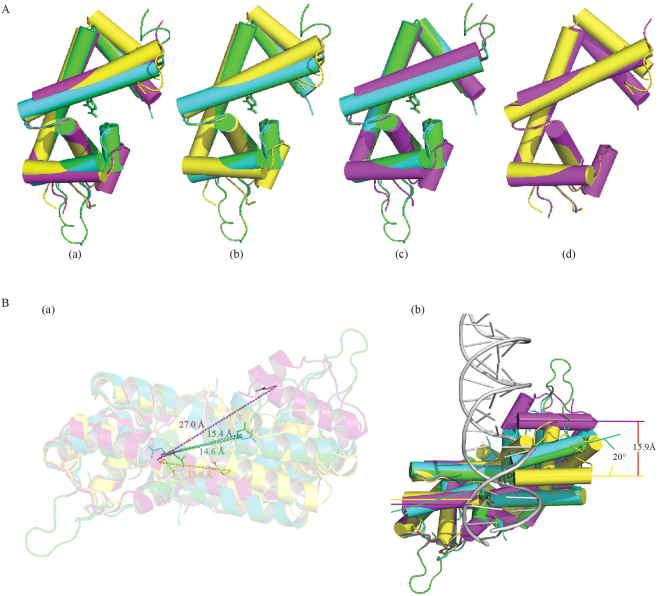
Figure 5.
Ligand binding induces significant conformational change in Rv2887. (A) (a) Monomeric structure superposition of apo (yellow), SA- (green), PAS- (blue) and DNA-bound (purple) Rv2887. (b) The binding of ligand SA/PAS induces the DNA binding domain (wHTH) to rotate up towards the dimerization interface by nearly 15~20°. (c) No significant conformational change was observed in the Rv2887 protomer upon ligand or DNA binding, except for the rotation of the wHTH domain. (d) The main difference between the apo and DNA-bound forms of Rv2887 is in the N-terminal. (B). Dimeric structure superposition of apo (yellow), SA- (green), PAS- (blue) and DNA-bound (purple) Rv2887. (a) Major differences between different dimers include different distances between the two DNA recognition helices (i.e. the distance between the Q64 and Q64′ Cα atoms) in different protein dimers (apo-: 13.6 Å; SA-:14.6 Å; PAS-:15.4 Å; DNA-: 27.0 Å). (b) Different orientations of the α4 helices in the ligand- or DNA-bound complexes result in different distortions of the dimer.