Figure 4.
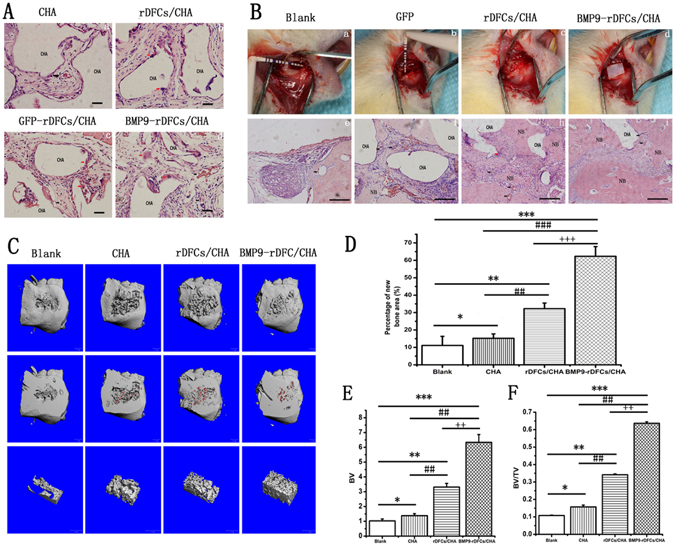
New bone formations in vivo. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining for sections of ectopic implantation. (B) The surgical procedure of implantation in alveolar bone defects of rats was showed in Fig. 4a,b,c,d. Hematoxylin and eosin staining for sections of new bone formation in alveolar bone defect in the down-panel of Fig. 4e,f,g,h. Blank bars: 5 μm. CHA: CHA scaffold materials. NB: new bone formation. Black arrow: blood vessel. Red arrow: macrophage. (C) The evaluation of new alveolar bone by Micro CT and 3D reconstruction. The morphology of new bone formation was revealed by 3D reconstructed images in blank group, CHA group, rDFCs/CHA group and BMP9-rDFCs/CHA group. CHA scaffolds were in red. (D) Percentage of new bone area. (E) BV: new bone volume. (F) BV/TV: new bone ratio of volume of new formation bone and volume of VOI. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to blank group, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared with CHA group, ++P < 0.01, +++P < 0.001 compared with rDFCs/CHA group.
