Figure 5.
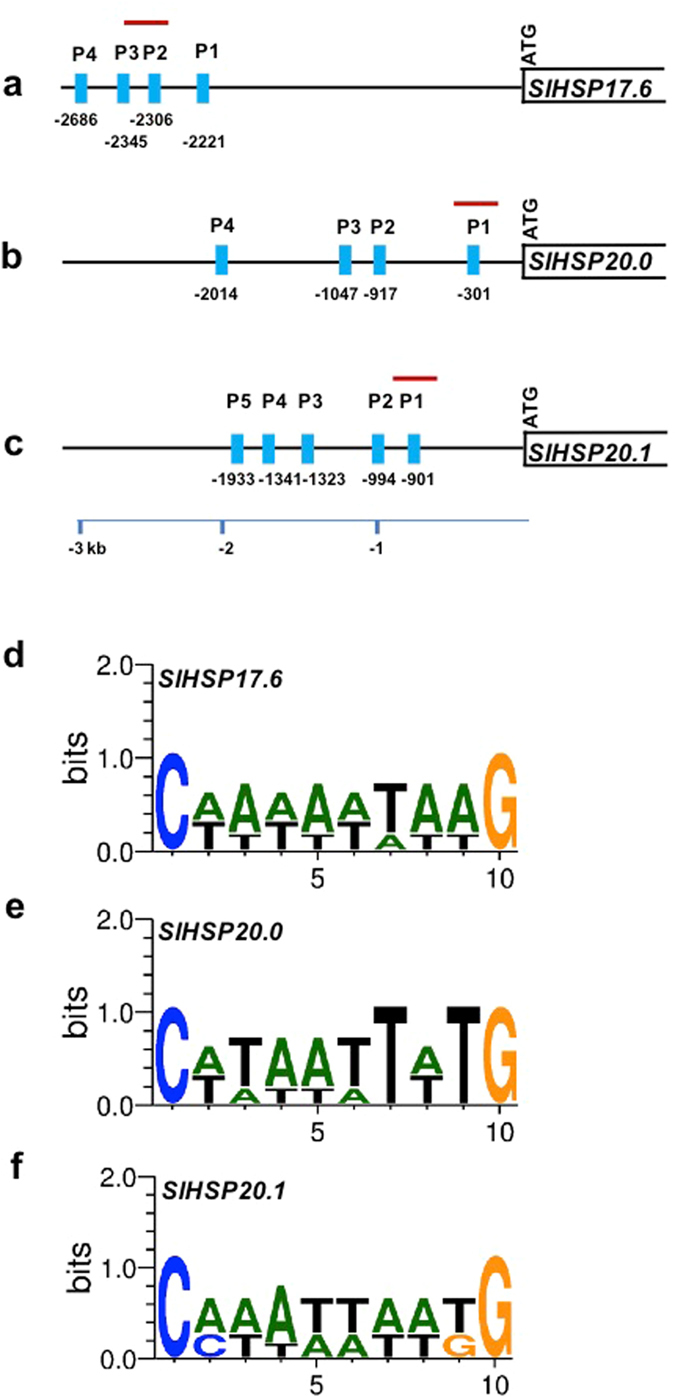
In silico analysis of class-I SlHSP (17.6, 20.0, 20.1) gene promoters. Promoter regions (≈3 kb of the 5′ upstream region of the start codon) of tomato SlHSP17.6, SlHSP20.0 and SlHSP20.1 genes were extracted using the International Tomato Genome Sequencing Consortium (SGN) database (version ITAG 2.4). Two databases, Plant CARE relational database35 and PLACE, the plant-cis-acting regulatory DNA elements database25 were used for plant cis-element search in the promoters of the described SlHSP genes. The possible RIN binding CArG-box motif sequences are [{C(C/T) (A/T)6(A/G)G}, {C(A/T)8G} and {C(C/T)(A/T)G(A/T)4 (A/G)G}]38, 39. All the CArG motifs found in SlHSP gene promoters are listed in Supplementary Table S2. The promoter position(s) significantly enriched in ChIP assay are highlighted with horizontal red line. (a) SlHSP17.6 gene promoter contains CArG cis element positions (here denoted as ‘P’), respectively at P1 (−2221), P2 (−2306), P3 (−2345) and P4 (−2686). (b) SlHSP20.0 gene promoter contains four CArG motifs positioned at P1 (−303), P2 (−917), P3 (−1047) and P4 (−2014), respectively. (c) SlHSP20.1 gene promoter harbors five CArG cis elements, positioned at P1 (−901), P2 (−994), P3 (−1323), P4 (−1341) and P5 (−1933). (d,e,f) show corresponding conserved locations and their distribution patterns in the 10 bp consensus sequence described in the text.
