Figure 5.
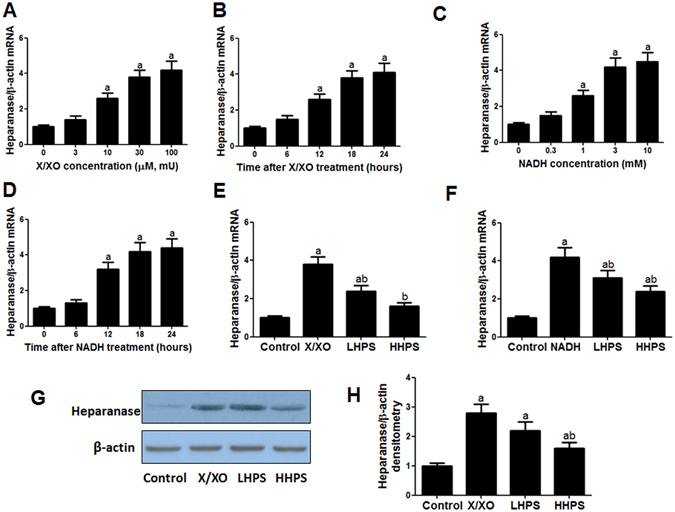
Hyperoside pre-treatment reduced the increased heparanase expression induced by ROS in cultured podocytes. (A) The dose-response effect of xanthine/xanthine oxidase (X/XO) on podocytes heparanase mRNA expression. Podocytes were incubated with 0, 3, 10, 30, 100 µM xanthine plus equal doses of xanthine oxidase (mU) for 18 h. (B) The dose-response effect of NADH on podocyte heparanase mRNA expression. Cultured podocytes were incubated with 0, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 mM NADH for 18 h. (C,D) Podocyte heparanase mRNA expression after incubation with X/XO (30 µM/mU) or NADH (3 mM) for 0, 6, 12, 18 and 24 h. (E) Hyperoside pre-incubation attenuated increased heparanase mRNA expression induced by extracellular ROS. Control: vehicle incubation for 18 h; X/XO: 30 µM xanthine plus 30 mU xanthine oxidase incubation for 18 h; LHPS or HHPS: 30 or 100 μg/ml hyperoside pre-incubation for 1 h and followed by X/XO (30 µM/mU) exposure. (F) Hyperoside pre-incubation attenuated increased heparanase mRNA expression induced by intracellular ROS. Control: vehicle incubation for 18 h; NADH: 3 mM NADH incubation for 18 h; LHPS or HHPS: 30 or 100 μg/ml hyperoside pre-incubation for 1 h and followed by NADH exposure. (G,H) Hyperoside pre-incubation attenuated heparanase protein expression induced by X/XO by western blot analysis. The columns showed the amount of heparanse protein levels relative to β-actin. Control: PBS incubation for 24 h; X/XO: X/XO (30 µM/mU) incubation for 24 h; LHPS or HHPS: 30 or 100 μg/ml hyperoside pre-incubation for 1 h and followed by X/XO (30 µM/mU) exposure. Data are presented as mean ± SD. P < 0.05 is statistically significant. aIndicates significant vs. Control, bindicates significant vs. ROS.
