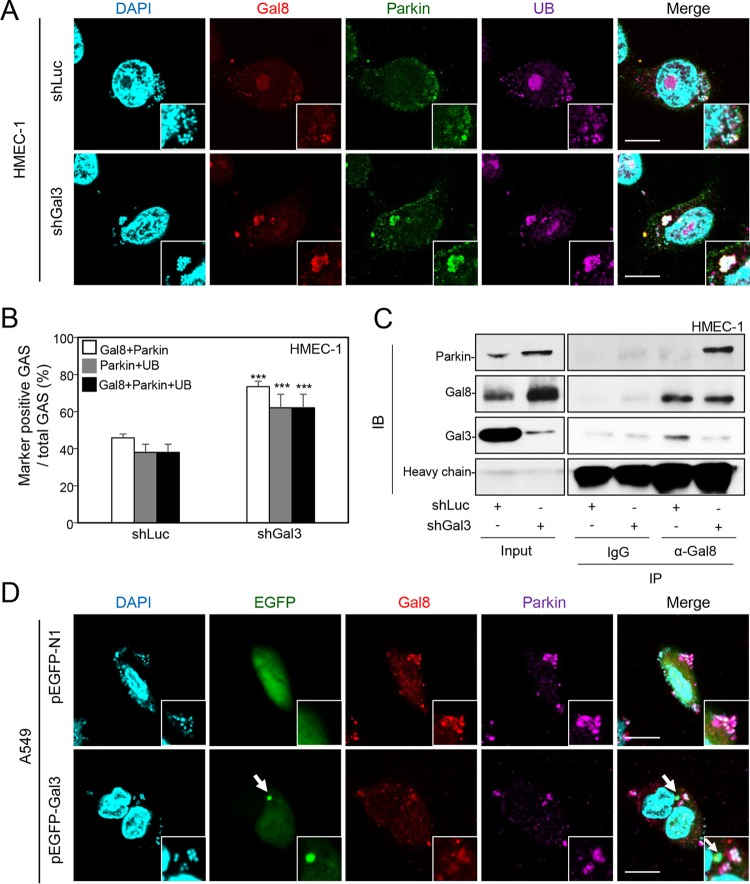
FIG 4 .
Gal-3 inhibits recruitment of Gal-8 and parkin, which interact with each other. (A) shLuc-HMEC-1 and shGal3-HMEC-1 cells were infected with GAS at MOI = 5 for 30 min, and gentamicin was added to kill extracellular bacteria. Cells were collected at 1 h postinfection and stained with anti-Gal-8, anti-parkin, and anti-ubiquitin (UB) antibodies. DAPI was used for cell nuclear and bacterial DNA staining. Images were observed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Levels of GAS surrounded with Gal-8, parkin, and UB were determined relative to total levels of intracellular GAS. All quantitative data represent the means ± SD of results from three independent experiments, and over 100 cells were counted in each sample. ***, P < 0.001 (compared to shLuc cells). (C) shLuc-HMEC-1 and shGal3-HMEC-1 cells were infected with GAS at MOI = 5 for 30 min, and gentamicin was added to kill extracellular bacteria. Cells were collected at 1 h postinfection, and immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using anti-Gal-8 antibody and goat control IgG followed by detection of parkin, Gal-8, and Gal-3 by Western blotting. The loading control was either whole-cell stain (Input) or IgG heavy chain. IB, immunoblot. (D) A549 cells were transfected with pEGFP-N1 or pEGFP-Gal3. Cells were further infected with GAS at MOI = 25 for 30 min, and gentamicin was added to kill extracellular bacteria. Cells were collected at 1 h postinfection and stained with anti-Gal-8 and anti-parkin antibodies. DAPI was used for cell nuclear and bacterial DNA staining. Images were observed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm.