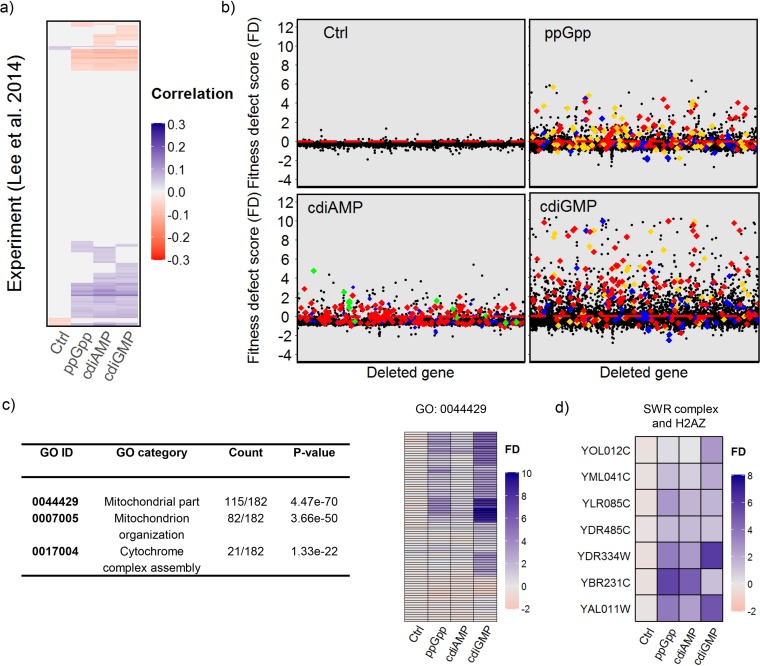
FIG 2 .
ppGpp, cdiAMP, and cdiGMP reduce the fitness of yeast mutants with compromised SWR1 complex activity or mitochondrial function. (a) Pearson correlation of FD scores with data from the chemogenomic experiments of Lee et al. (33). Only significant correlations are shown (q ≤ 0.01). (b) Change in colony size induced by the synthesis of each nucleotide in each mutant. Colored points correspond to selected chemogenomic profile signature groups of Lee et al. (33) and indicate the highest positive correlations with the SGA fitness profiles observed for the bacterial nucleotides. Gold, mitochondrial stress; green, tubulin folding and SWR complex; red, minor response 78; blue, translation. (c) Gene ontology analysis of the genes in the minor response 78 signature showed significant enrichment for mitochondrial functions. The heat map shows FD scores for the 115 genes from this signature which were in the mitochondrial portion of the GO category (0044429), indicating marked fitness defects, particularly in the presence of ppGpp and cdiGMP. (d) Heat map of FD scores for 6 genes belonging to the SWR1 complex that showed negative, synthetic sick interactions with the synthesis of each nucleotide. The negative interaction with HTZ1 (YOL012C) encoding the H2AZ histone variant exchanged by the SWR1 complex is also shown.