Figure 2.
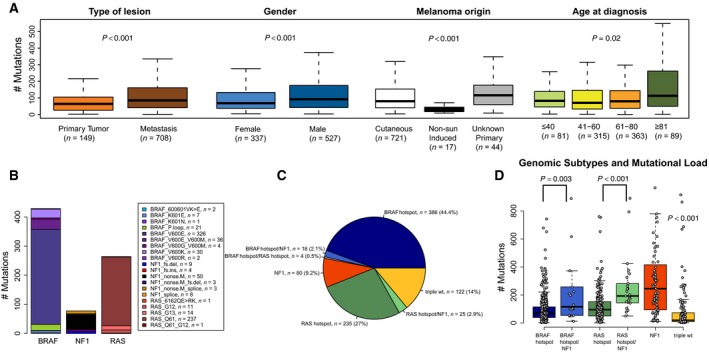
Mutational burden in association with clinical parameters in 864 melanoma tumors. (A) The total number of somatic mutations (coding and non‐coding) was determined for each patient and further correlated to clinical factors such as tumor type, melanoma origin, gender and age. (B–D) Genetic activation of the MAPK pathway in melanoma (n = 870). A schematic overview of selected MAPK mutations in BRAF,RAS and NF1 with each gene was analyzed separately with no consideration of cross gene co‐occurring events (B). The melanoma samples were further classified into mutational subtypes based on hotspot mutations in BRAF (affecting amino acid V600 and/or K601), RAS (Q61, G12, G13) or any non‐synonymous mutation in NF1 (C), and correlated to mutational burden (D). Non‐parametric Kruskal–Wallis and Wilcoxon tests were used to calculate P‐values (A and D).
