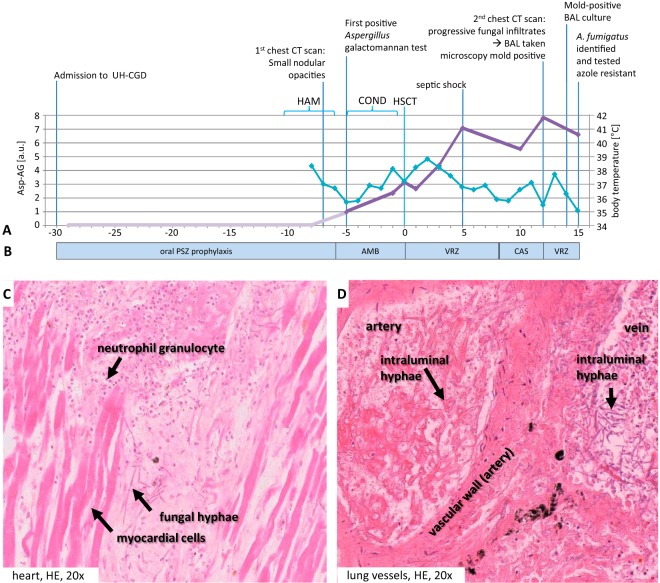
FIG 1.
Time course of diagnostic and therapeutic events. (A) Diagnostic parameters. On the primary y axis, the Bio-Rad Platelia Aspergillus galactomannan antigen test results (Asp-AG; light and dark purple lines) are shown. On the secondary axis, body temperatures (light blue) are shown. UH-CGD, University Hospital Carl Gustav at the Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany; HAM, high-dose cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone salvage therapy (mitoxantrone at 30 mg/m2/day i.v. q.d. and high-dose cytarabine at 2,000 mg/m2/day i.v. b.i.d., days 1 and 5 before conditioning chemotherapy, corresponding to days −11 and −7 with respect to HSCT); COND, conditioning chemotherapy with ATG (10 mg/kg/day i.v. q.d., days −5 to −2; Fresenius, Bad Homburg, Germany), fludarabin (30 mg/m2/day i.v. q.d., days −6 to −2), and melphalan (150 mg/m2 i.v. q.d., day −2); HSCT, day of human stem cell transplantation (day 0); a.u., arbitrary units. (B) Antifungal management. Posaconazole (PSZ) prophylaxis was at 200 mg p.o. b.i.d. Liposomal amphotericin B (AMB) was at 3 mg/kg/day i.v. q.d. Voriconazole (VZR) was at 4 mg/kg/day i.v. b.i.d., with a loading dose of 6 mg/kg/day i.v. b.i.d. (day 0 and day 12, respectively). Caspofungin (CAS) was at 50 mg i.v. q.d., with a loading dose of 70 mg i.v. q.d. (day +9). (C, D) Postmortem analyses. (C) Fungal abscess in the anterior cell wall of the heart with surrounding granulocytic reaction; (D) vascular invasive growth and detection of dichotomously branched and septate fungi in the lumens of lung vessels. HE, hematoxylin and eosin.