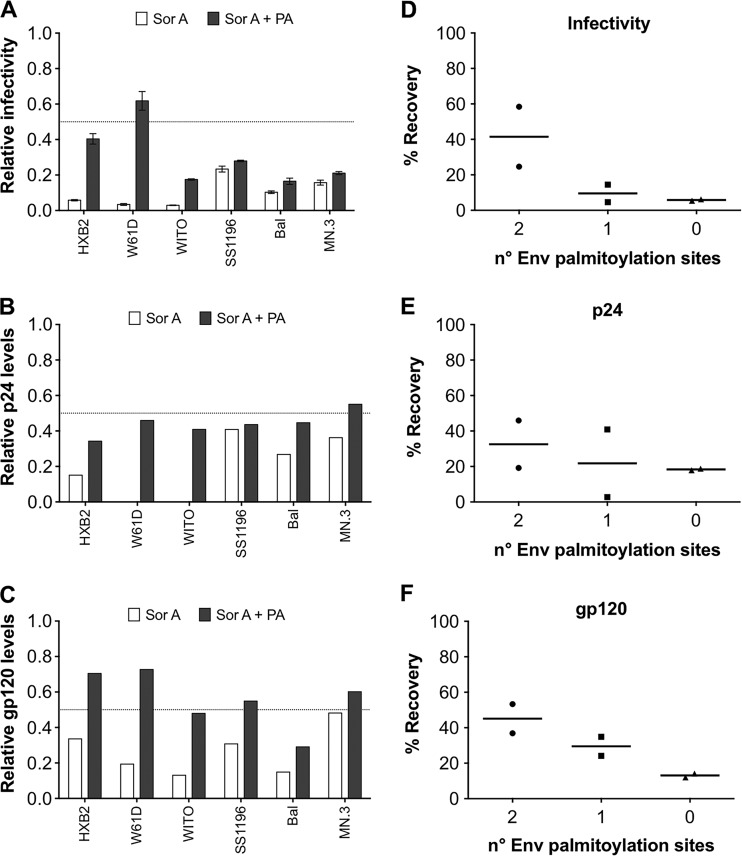
FIG 3.
Palmitic acid (PA) restores the SorA-mediated inhibition of infectious HIV production. Effect of SorA on produced HIVpp infectivity (A), p24 content (B), and gp120 content (C) (white bars) and the respective recovery by PA addition (black bars). HIVpp with Env proteins that carry mutations in the gp41 palmitoylation sites Cys764/Cys837 were produced from 293T cells in the presence of SorA 10 μM or DMSO control (vehicle) and tested for infectivity and p24 and gp120 content. Reductions and recovery levels by PA addition are shown as normalized values relative to the DMSO or DMSO+PA controls, respectively. The Env proteins of the HIVpp differ in the number of palmitoylation sites at residues 764/837 and have the following features: Cys764/Cys837 in HXB2 and W61D, Cys764/no Cys837 in WITO, no Cys764/Cys837 in SS1196, and no Cys764/no Cys837 in BaL and MN.3. The percent recovery was calculated by subtracting the mean infectivity (from three independent experiments), p24 values, or gp120 values of samples not treated with PA from the values of the samples treated with PA for each virus. The percentages of PA-mediated recovery of virus infectivity (D), p24 (E), and gp120 (F) related to the number of palmitoylation sites are shown. The dotted lines highlight half relative levels. Values for B and C are derived from Western blot quantification of p24 and gp120, respectively. Single concentrations of compounds were chosen based on inhibitory extent and lack of toxicity.