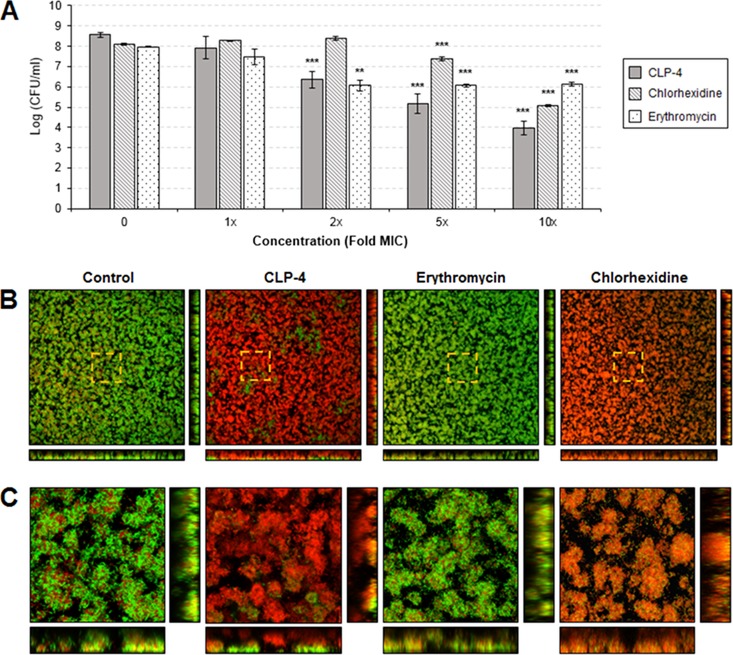
FIG 5.
Effects of CLP-4 on preformed biofilms. S. mutans UA159 biofilms were established for 24 h and then treated with increasing concentrations (1× to 10× the MIC) of CLP-4, chlorhexidine, or erythromycin. (A) Antibiofilm activities were assessed by quantifying the cell viability of treated biofilms by colony enumeration on agar plates. The means and standard deviations of three biological replicates from three independent experiments are shown. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 compared to untreated control. (B) Biofilms treated with 10× the MICs for each antimicrobial were fluorescently labeled using the LIVE/DEAD BacLight viability stain and visualized by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Shown are the top-down three-dimensional (3D) volume rendering of biofilms at a total magnification of ×400. Bottom images represent optical planes in the xz, and vertical thin images represent yz dimensions. Membrane-compromised bacteria are stained red with propidium iodide, while intact bacteria are stained green with SYTO 9. Areas highlighted by dashed lines indicate regions of interest (ROIs) viewed at a higher magnification. Dimensions shown are 387.5 μm by 387.5 μm by 16 μm. (C) ROIs are presented at ×2,300 magnification. Dimensions shown are 68.1 μm by 68.1 μm by 16 μm.