Figure 5.
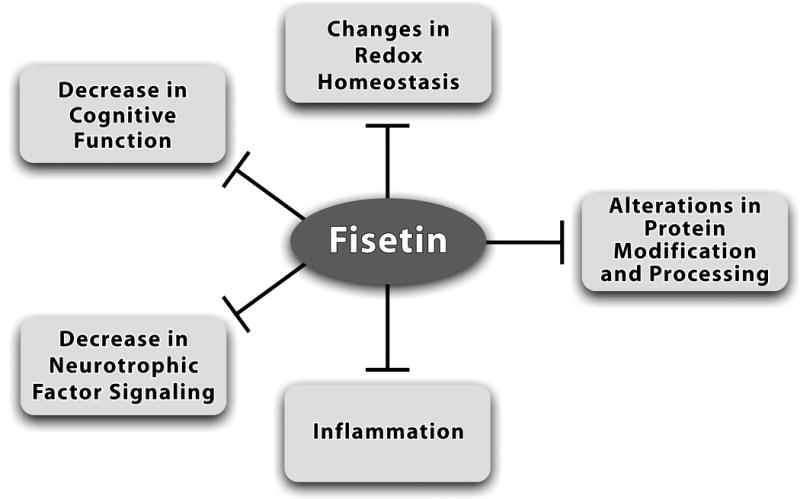
Fisetin affects multiple pathways implicated in brain aging and age-associated diseases. As discussed in this article, fisetin can increase brain cell function and survival through maintenance of redox homeostasis, activating neurotrophic factor signaling pathways and inhibiting inflammatory responses. Fisetin can also enhance cognitive function and in some cases, modulate proteasome activity. Therefore, it has the potential to act as a multi-factorial therapeutic for reducing the decline in brain function associated with age-associated neurological diseases.
