Figure 1.
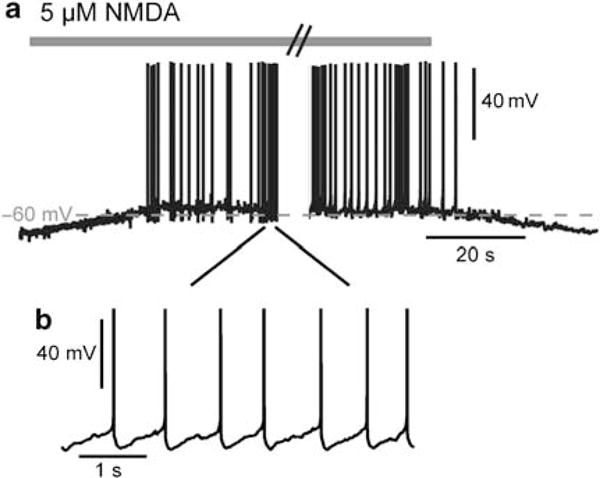
Membrane potential transition from a hyperpolarized resting potential to a depolarized plateau potential of a medium spiny neuron (MSN) in response to glutamatergic receptor stimulation. (a) Transition in a representative MSN recorded in an acute slice in perforated-patch clamp. Application of 5 μM N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), which mimics cortical synaptic inputs, evoked a reversible membrane potential transition between a hyperpolarized state and a depolarized plateau potential inducing a continuous action potential firing. (b) Periodic spike firing of MSN during the 5 μM NMDA-induced upstate.
