Figure 7. Germline chromatin decompaction in morc-1(−) mutants is met-1-dependent. (A).
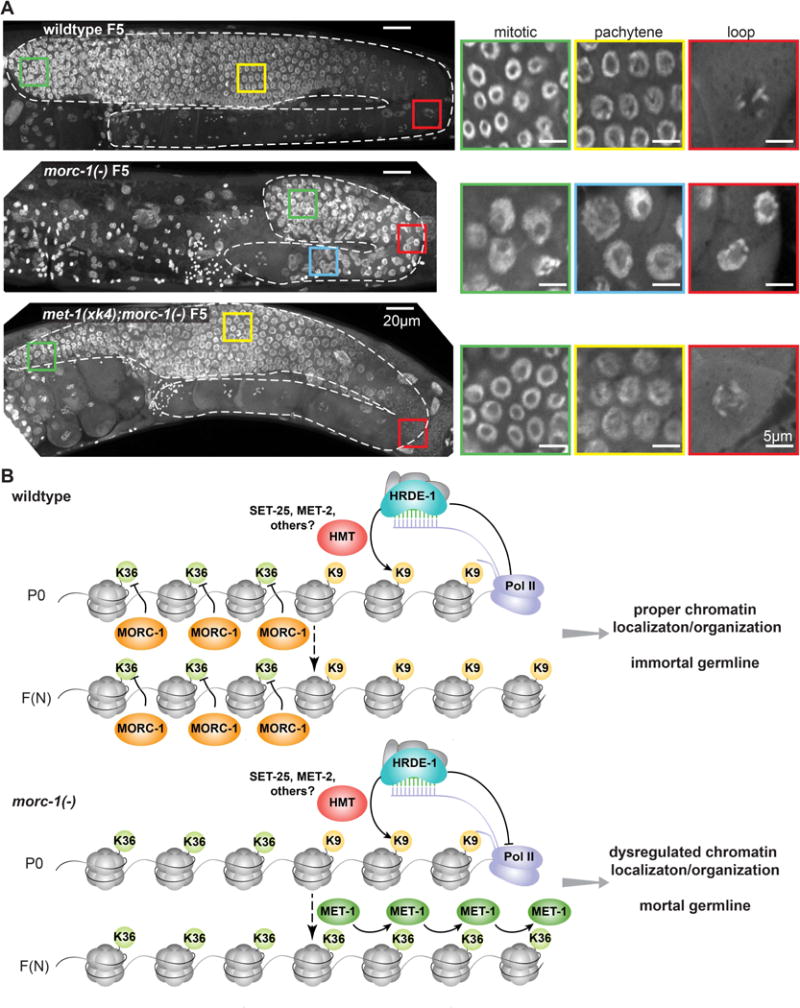
Whole mount DAPI staining of wildtype, morc-1(−), and met-1(xk4);morc-1(−) worms at F5 at 25°C. morc-1(−) worms are sterile. Left: maximum projection images from top to bottom of the germline. The germline is outlined in dashed white lines; colored boxes indicate location of insets shown at right. Right: single plane from the indicated region. Due to chromatin disorganization in morc-1(−) mutants, we cannot distinguish mitotic and pachytene regions based on nuclear morphology. (B) Model for MORC-1-mediated regulation of transgenerational chromatin marks at HRDE-1-target loci. In wildtype worms, MORC-1 restrains the spread of H3K36me3 into H3K9me3-marked endo-siRNA targets, allowing H3K9me3 to be maintained in subsequent generations. In morc-1(−) mutants, MET-1 mediates the spread of H3K36me3 to these targets, causing progressive loss of H3K9me3 and germline mortality.
