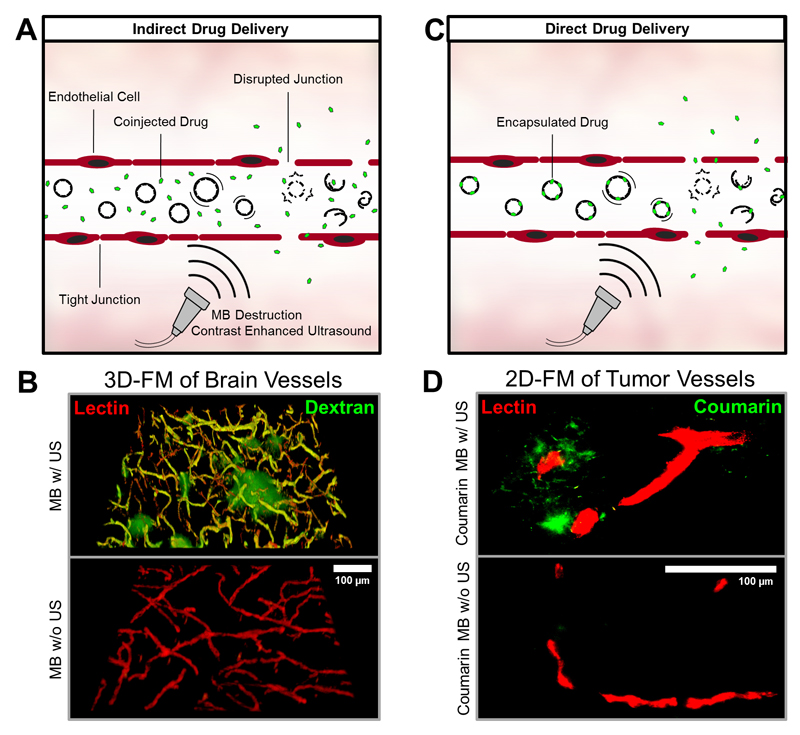
Figure 4. PBCA-based polymeric MB for indirect and direct drug delivery.
A+C: After i.v. injection, MB can be used to enhance the permeability and penetration of co-administered (A: indirect drug delivery) or co-formulated (B: direct drug delivery) drugs and drug delivery systems. B: Ex vivo two-photon laser scanning microscopy (3D-FM) of the extravasation of the macromolecular model drug FITC-dextran (green) across the blood-brain barrier. Rhodamine-lectin-stained blood vessels are shown red. Upon US-induced MB destruction (upper panel), the accumulation and penetration of FITC-dextran can be clearly detected in the mouse brain. No FITC-dextran extravasation is observed if US is omitted (lower panel). D: Ex vivo fluorescence microscopy (2D-FM) images of coumarin 6 (green) accumulation, released from the MB shell or entrapped within MB shell fragments, in subcutaneous CT26 colon carcinoma tumors in mice, in relation to rhodamine-lectin-stained tumor blood vessels (red). Upon US-mediated MB destruction of VEGFR-2-targeted and coumarin 6-loaded MB, substantially enhanced model drug delivery to and into tumorous tissue can be observed.