Figure 7. IKKε is critical for the anti-viral function of SPL during IAV infection.
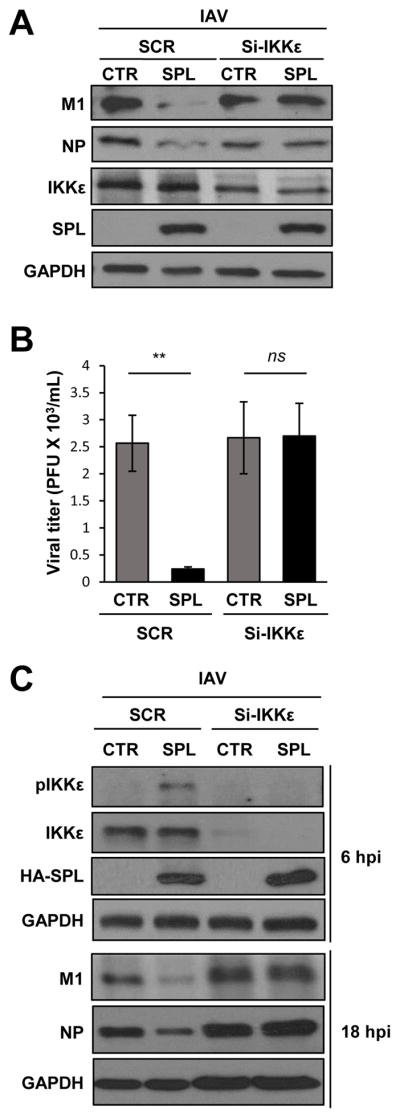
(A) SPL KO-1 cells (2 X 105) were transfected with si-RNA specific to IKKε (si-IKKε) or non-specific scrambled (SCR) si-RNA in the presence of SPL or empty vector control (CTR). Transfected cells were infected with IAV at an MOI of 0.1. At 1 dpi, Western blotting was performed to detect M1, NP, IKKε, HA-SPL, and GAPDH. (B) KO-2 cells (2 X 105) were transfected with si-IKKε or non-specific scrambled (SCR) si-RNA in the presence of SPL or empty vector control (CTR). Transfected cells were infected with IAV at an MOI of 0.1 and then at 24 hpi, the supernatants were collected to quantify viral titers by plaque assay on MDCK cells. Three separate samples of virus-infected cells per group were used for each condition. Values are means ± SEM (n = 3/group; **, P ≤ 0.01). (C) A549 cells (2 X 105) were transfected with si-RNA specific to IKKε (si-IKKε) or non-specific scrambled (SCR) si-RNA in the presence of SPL or empty vector control (CTR). Transfected cells were infected with IAV at an MOI of 0.5. At 6 hpi, Western blotting was performed to detect pIKKε, IKKε, HA-SPL, and GAPDH and at 18 hpi, Western blotting was performed to detect viral M1, NP, and GAPDH.
