Figure 5.
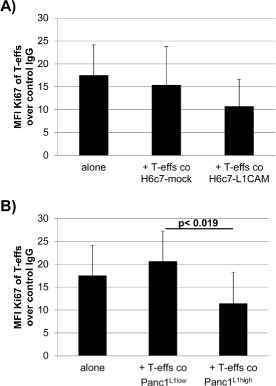
In the presence of L1CAM T‐effs acquire an immunosuppressive phenotype. T‐effs were cocultured for 72 h with T cell activation/expansion beads and in the presence of (A) H6c7‐mock and H6c7‐L1CAM cells or (B) Panc1L1low and Panc1L1high cells, respectively. Then, autologous T‐effs (T‐effsa) that had been cultured in parallel, were cultured together with one of the cocultured T‐eff populations at a ratio of 75:1 and in the presence of T cell activation/expansion beads for further 72 h. T cells were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry for expression of Ki‐67. Data are presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) over control. Means ± SD from 5 to 6 experiments are shown. Statistical significance is indicated by the respective p‐values. C) Representative histograms from Ki‐67 stainings of T‐effsa cocultured with T‐effs from cocultures with H6c7‐L1CAM cells without depletion of CD25+ T cells (T‐effs), with depletion of CD25+ cells (CD25− Teffs). As control, T‐effsa were cocultured under similar conditions with enriched CD25+ T cells (CD25+ T‐effs) or T‐regs that had been cocultured with H6c7‐L1CAM cells before. D) After coculture with H6c7‐mock or H6c7‐L1CAM cells, T‐effs were stained for CD25, CD69 and membrane‐bound TGF‐β1. Representative histograms from TGF‐β1 stainings in CD25−CD69+ T‐effs are shown. E) Levels of IL‐2, IL‐12p40 and SDF‐1α were determined in supernatants from T‐effsa cultured either alone or together with T‐effs that had been cocultured with H6c7‐L1CAM cells before. Data from one representative experiment are shown.
