Figure 2.
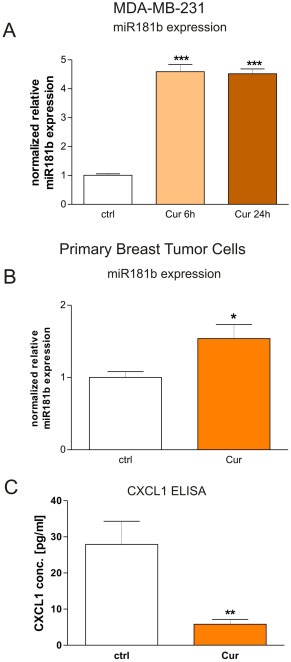
Curcumin modulates miR181b expression in human breast cancer cells. A: Quantitative RT‐PCR reveals that human metastatic breast cancer cells (MDA‐MB‐231) treated with Curcumin for 6 h (“Cur”) express four fold higher amounts of miRNA181b in respect to carrier‐treated cells (“ctrl”). ***P < 0.001, student's t‐test. B: miR181b expression was analyzed in breast cancer cells from human primary tumor samples, cultured in vitro and treated for 24 h with Curcumin with respect to carrier‐treated control cells from the same origin. For each case, we observed up‐regulation of miR181b after Curcumin treatment (data not shown) and by pooling the results from all patient data we obtained a mean miR181b up‐regulation rate of 50%, which was statistically significant (*p < 0.05; student's t‐test). Mean + SD from 3 different patients are shown. C: CXCL1 protein expression secreted from breast cancer cells isolated from primary human tumors that were treated with Curcumin in vitro was analyzed by ELISA. CXCL1 concentrations were statistically significantly down‐regulated about 3.5‐fold in Curcumin treated tumor cells (**p < 0.01; student's t‐test). Mean + SD from 3 different patients are shown.
