Figure 4.
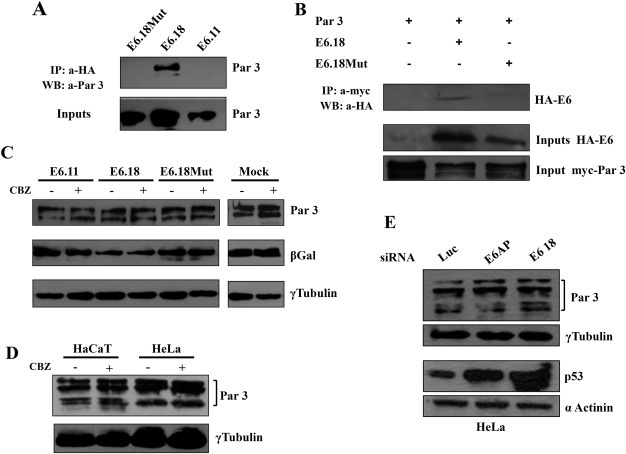
HPV‐18 E6 oncoprotein targets Par3 protein in vivo without inducing proteasome‐mediated degradation. A. High‐risk HPV‐18 E6 proteins in vivo interact with Par3. HEK293 cells were transfected with myc‐Par3 plasmid in the presence of HA‐E6.11, HA‐E6.18 and HA‐E6.18 Mut. Equal amounts of protein, extracted after 24 h, were either resolved directly (input) or immunoprecipitated with anti‐HA antibody followed by binding to Protein A‐Sepharose affinity beads. Following SDS‐PAGE, whole cell lysates (inputs, lower panel) and Protein A‐Sepharose bound complexes (upper panel) were probed with anti‐Par3 antibody. B. The same as panel A but cell extracts were analysed for myc‐Par3 and HA‐ E6 protein inputs or immunoprecipitated with anti‐myc resin. C. Expression of E6.18 oncoprotein does not affect Par3 protein levels. HEK293 cells were transfected with the Par3 expression plasmid in the absence (mock) or presence of E6.11, E6.18, or E6.18 Mut. After 24 h, cells were incubated for 2 h with or without CBZ proteasome inhibitor as indicated. Proteins were then extracted and equal amounts were separated by SDS‐PAGE. Protein levels were ascertained by western blotting analysis with anti‐Par3 (upper panel) or anti‐γ tubulin antibodies (as loading control, lower panel). The expression of β‐Gal was used as a control for transfection efficiency (middle panel). D. Par3 protein levels are not regulated by the proteasome pathway. HaCat and HeLa cells were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the proteasome inhibitor CBZ. The level of Par3 proteins were then ascertained by western blotting using anti‐Par3 antibody (upper panel). γ tubulin levels were determined as loading control, lower panel. E. The levels of Par3 protein do not change in HeLa cells upon E6.18 ablation. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA directed against luciferase, E6AP or E6.18. After 48 h, cells were harvested and protein levels were assessed by western blotting using anti‐Par3 antibody, anti‐p53 (for control of E6.18 silencing) and anti‐γ tubulin or α‐actinin, for monitoring protein loading.
