Figure 4.
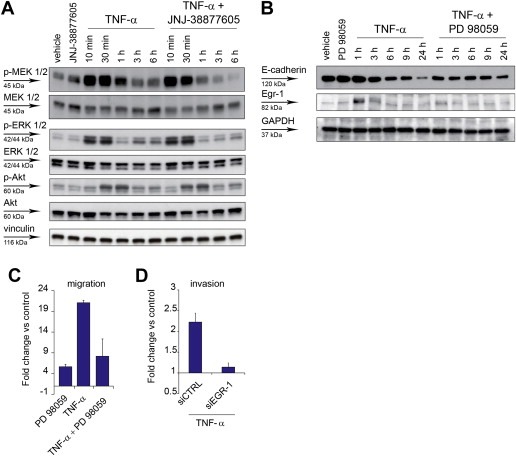
TNF‐α sustains the MEK‐ERK pathway through MET, and the MEK‐ERK pathway is required for cell invasion. (A) Western blot showing phosphorylation of MEK1/2 (p‐MEK 1/2), p42/44 ERK 1/2 (p‐ERK 1/2), and Akt (p‐Akt), and the respective total proteins, at the indicated time‐points after A549 treatment with TNF‐α (10 ng/ml), in the absence or in the presence of JNJ‐38877605 (500 nM). Vinculin was probed as control of equal protein loading. (B) Western blot showing E‐cadherin and Egr‐1 expression at the indicated time‐points after A549 treatment with TNF‐α (10 ng/ml), in the absence or in the presence of the MEK inhibitor PD 98059 (20 μM). GAPDH was probed as control of equal protein loading. (C) A549 cell migration assessed in Transwell assay 24 h after treatment with TNF‐α (10 ng/ml), in the absence or in the presence of PD 98059 (20 μM). Graphs represent the fold change vs. control (untreated cells) of the number of migrating cells. Bars: mean of three independent experiments ± SEM. (D) A549 cell invasion assessed in Transwell assay 24 h after treatment with TNF‐α (10 ng/ml), in cells transfected 48 h before with siRNA against EGR‐1 (siEGR‐1) or control siRNA (siCTRL). Graphs represent the fold change vs. control (untreated cells) of the number of invading cells. Bars: mean of three independent experiments ± S.E.M.
