Figure 3.
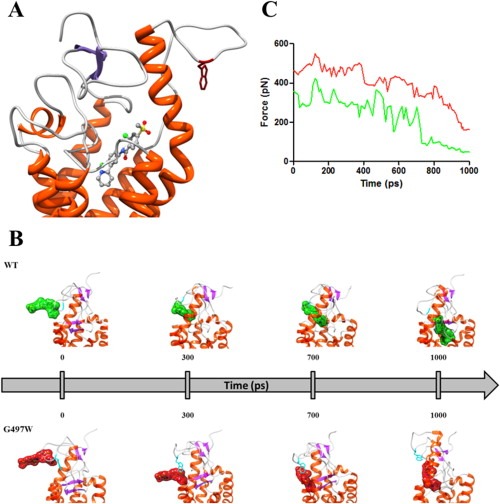
(A) Zoomed view of the SMOG497W binding site in complex with vismodegib. The receptor is shown as a secondary‐structure colored ribbon (orange, α‐helices; purple, β‐sheets; gray, coils). Vismodegib is portrayed as atom‐colored sticks‐and‐balls (red, O; blue, N; green, Cl; S, sulfur; gray, C). Residue W497 is evidenced as dark red sticks. Hydrogen atoms, water molecules, ions and counterions are omitted for clarity. (B) SMD snapshots of vismodegib entering the receptor binding pocket. Vismodegib is highlighted by its green/red van der Waals surface. Hydrogen atoms, ions, counterions and water molecules are omitted for clarity. (C) Rupture force vs. time during the entry process of vismodegib within the WT (green) and SMOG497W (red) binding site.
