Figure 4.
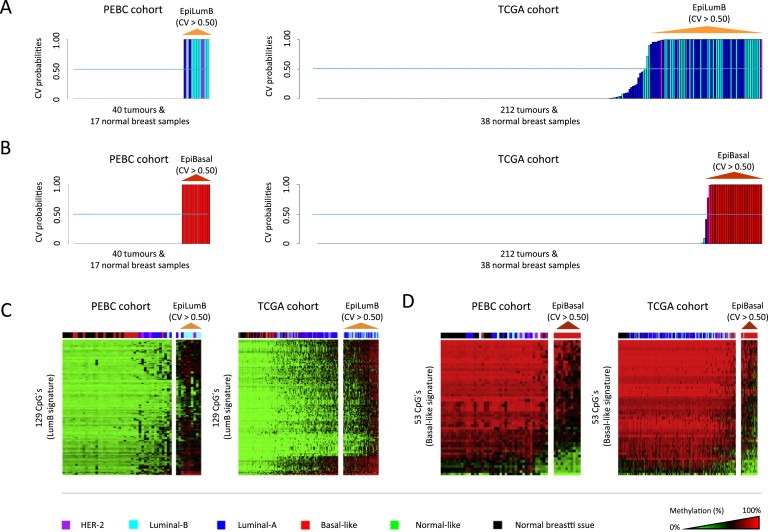
The definition of DNA methylation‐based subtypes in breast tumors. A) Cross‐validated probability values derived from a well‐established pattern recognition algorithm (PAMr implemented in R) indicating how robustly each tumor displays the validated signature of LumB‐associated CpG island promoter methylation events (based on the validated catalogue of LumB‐associated CpG island promoter methylation events, i.e. the 129 CpG's indicated in Figure 3C). The barplots show the probability values on the y‐axis for each tumor ordered on the x‐axis from left to right according to the probability values from low to high, respectively, for each of the two cohorts i.e. the PEBC cohort (barplot on the left) and the TCGA cohort (barplot on the right). Tumors scoring positive for this signature have a cross‐validated probability >0.50 as indicated by the dashed line over each of the two barplots. The color of each bar (representing tumors) is indicative of the expression‐based subtype as given at the bottom of the figure. B) The cross‐validated probability values derived from PAMr indicating how robustly each tumor displays the Basal‐like associated gene body hypomethylation signature (based on the 53 CpG's as indicated in the lower panel of Figure 3B) shown for both the PEBC (left) and TCGA cohorts (right). C) DNA methylation data over the validated catalogue of 129 “hallmark” CpG's characteristic of LumB tumors (i.e. those identified within CpG island promoters in association with the LumB subtype consistently in both the PEBC and TCGA cohorts) shown with respect to the novel Epi‐LumB subtype. The expression‐based subtypes are shown according to the color scheme displayed at the bottom of the figure. D) Similarly, the DNA methylation data over the validated catalogue of 53 “hallmark” CpG's characteristic of Basal‐like tumors (i.e. gene body CpG's consistently associated with Basal‐like tumors in both the PEBC and TCGA cohorts) are shown with respect to the novel Epi‐Basal subtype.
