Figure 6.
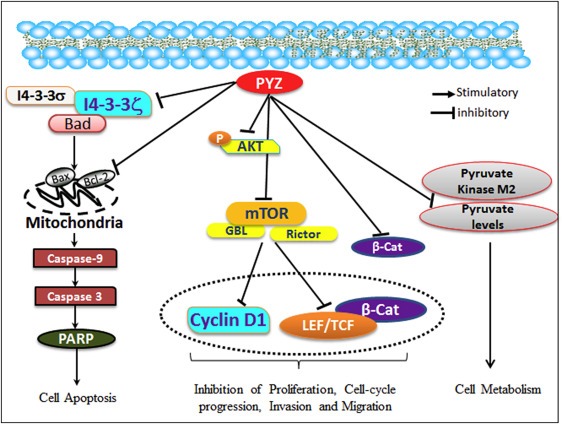
Working model of pyrithione zinc in oral cancer. PYZ modulates directly or indirectly the major proteins implicated in oral carcinogenesis, proliferation, invasion, migration, cell cycle progression, apoptosis and metabolism. PYZ induced upregulation of pro‐apoptotic BAX and BAD is indicative of release of cytochrome C from mitochondria which further activates Caspase‐3, Caspase‐9 and PARP, suggesting caspase dependent apoptosis. Treatment with PYZ also downregulated the expression of 14‐3‐3ζ and 14‐3‐3σ proteins, which have been previously shown to be implicated in oral carcinogenesis. PYZ treatment also decreased pAkt levels and downregulated DKK3, β‐catenin, LEF1, TCF1, and its target cyclin D1 and c‐Myc suggesting inhibition of Wnt/β‐catenin signaling pathway. PYZ treatment also downregulated mTOR, GβL, Rictor, and Raptor, suggesting inhibition of the mTOR pathway in PYZ treated oral cancer cells. PYZ inhibited pyruvate levels and PKM2, suggesting inhibition of the metabolic activity in PYZ treated oral cancer cells.
