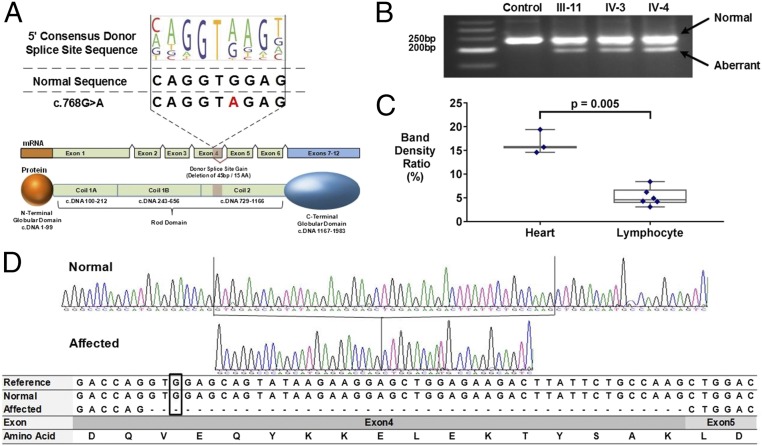
Fig. 4.
A rare synonymous LMNA variant creates a novel splice donor sequence in Exon 4. (A) Comparison of the 5′ donor consensus splice signal sequence with the LMNA reference (c.768 G, MaxEnt score = 2.6) and variant (c.768 A; MaxEnt score = 7.1). A ΔMaxEnt score (+4.5) predicted the gain of a novel splice donor in LMNA exon 4. A schematic showing premature splicing of the terminal end of exon 4 corresponds to a 15-aa deletion within coil 2 of the LMNA rod domain. (B) Gel fractionation of RT-PCR products of cardiac RNA detects a normal and smaller transcript in synonymous variant carriers. (C) The ratio of normal and aberrant splicing quantified by densitometric analyses of the gel-fractionated RT-PCR products in cardiac tissue (n = 3) and lymphocyte (n = 6) RNA demonstrates threefold more misspliced RNA in cardiac tissue (P = 0.005, two-sided t test) than in lymphocytes. (D) The sequence traces of RT-PCR products from a normal and an affected individual as well as aligned sequences of RT-PCR products to the reference mRNA of LMNA. The normal band from mRNA of LMNA c.768 G > A subject includes all nucleotides present in the reference, and the aberrant band deletes 45 bp in the end of exon 4.