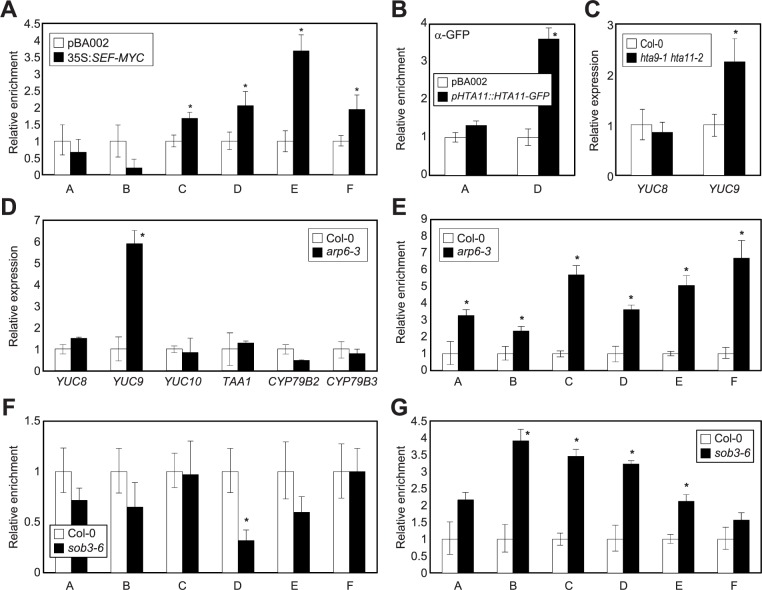
Fig 4. Regulation of YUC9 expression by the SWR1 complex.
(A) Binding of SEF to the YUC9 promoter. Two-week-old 35S:SEF-MYC transgenic plants grown under LD conditions were used to conduct ChIP assays. (B) H2A.Z deposition in the YUC9 promoter. Two-week-old pHTA11::HTA11-GFP transgenic plants grown under LD conditions were used for ChIP analysis with anti-GFP antibody. Eluted DNA was subject to qPCR analysis. (C and D) Transcript accumulation of YUC9 in the genetic mutants of H2A.Z exchange. Nine-day-old hta9-1 hta11-2 (C) and arp6-3 (D) mutants grown under LD conditions were used to examine transcript accumulation. Three biological replicates were averaged and statistically analyzed by two-tailed Student's t-test assuming unequal variance (*P < 0.05). (E) Recruitment of Pol II at the YUC9 promoter in arp6-3. Two-week-old plants grown under LD conditions were used to conduct ChIP assays with an anti-N-terminus of Arabidopsis Pol II antibody. (F) H2A.Z deposition at the YUC9 promoter in sob3-6. Two-week-old plants grown under LD conditions were used to conduct ChIP assays with an anti-H2A.Z antibody. (G) Recruitment of Pol II at the YUC9 promoter in sob3-6. Two-week-old plants grown under LD conditions were used to conduct ChIP assays with an anti-N-terminus of Arabidopsis Pol II antibody.