Fig. 4. Flower coloration, anthocyanin composition, and transgene expression in transgenic ‘Sei Arabella’.
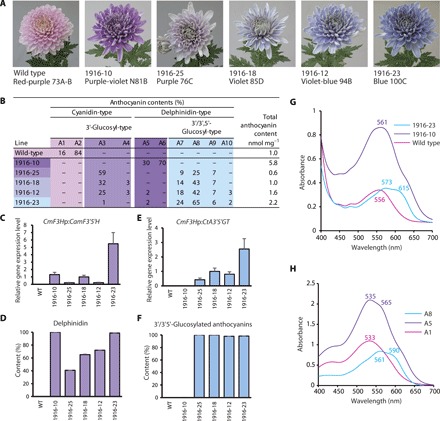
(A) Pictures of representative flower colors of wild-type and transgenic lines. Each line presents the color group and number of RHS Colour Charts. (B) Anthocyanin composition. (C and D) Relative expression of CamF3′5′H (C) and the resultant delphinidin-based anthocyanins (D). Contents of delphinidin-based anthocyanins corresponded well with the expression of CamF3′5′H. (E and F) Relative expression of CtA3′5′GT (E) and the resultant 3′/3′,5′-glucosylated anthocyanins (F). Contents of 3′/3′,5′-glucosylated anthocyanins corresponded well with the expression of CtA3′5′GT. (G) Visible absorption spectra of fresh petals of wild-type (pink), 1916-10 (purple), and 1916-23 (blue) lines. (H) Visible absorption spectra of major anthocyanins derived from pink (A1; wild type), purple-violet (A5), and blue/violet-blue (A8) chrysanthemums in acetate buffer (pH 5.6).
