Figure 6.
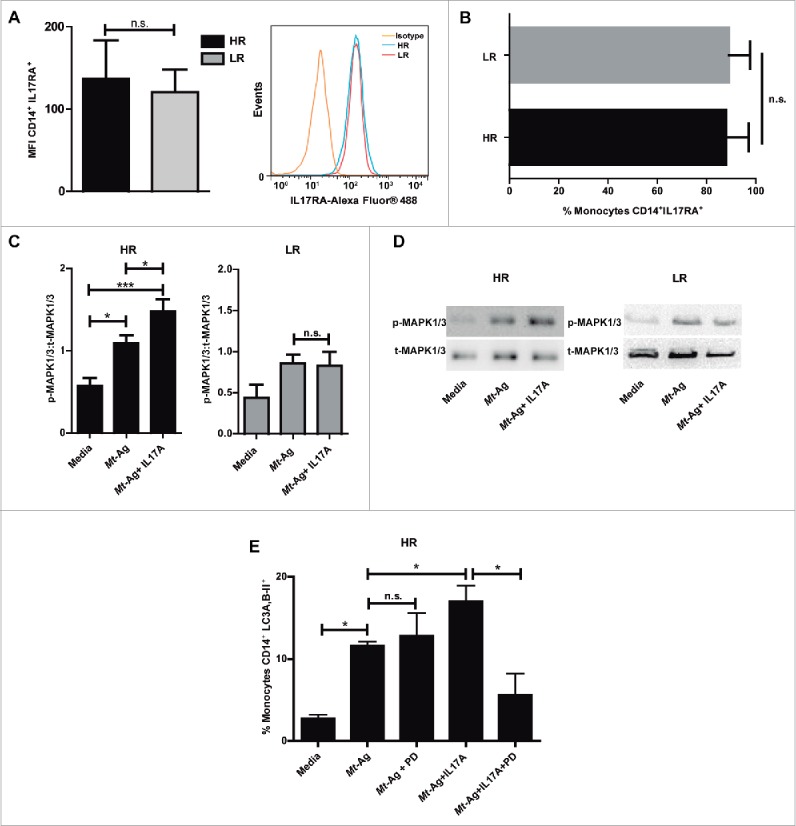
IL17 receptor signaling promotes autophagy through MAPK1/3 in high-responder TB patients. (A and B) IL17RA levels were evaluated by flow cytometry in CD14+ monocytes from HR TB and LR TB patients. (A) Bars represent the MFI (mean fluorescence intensity) ± SEM and a representative histogram of flow cytometry is shown. (B) Bars represents the percentage of CD14+ IL17RA+ cells ± SEM (C and D) Adherent cells from HR TB and LR TB were stimulated with sonicated M. tuberculosis antigen (Mt- Ag, 10 µg/ml) ± recombinant IL17A (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. Phosphorylated and total MAPK1/3 expressions were then measured by western blot. (C) Densitometry of the images was performed, and the ratios of p-MAPK1/3 to t-MAPK1/3 protein expression were expressed as arbitrary units. (D) Results from a representative HR and a LR TB patient are shown. (E) PBMC from HR TB were incubated with or without an inhibitor of activation of MAPK1/3 (PD98059 [PD], 50 μM) for 1 h and then stimulated with sonicated M. tuberculosis (Mt- Ag, 10 µg/ml) ± recombinant IL17A (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. Autophagy levels were evaluated by flow cytometry against intracellular saponin-resistant LC3A,B-II on CD14+ cells. Bars represent the mean values of the percentage of CD14+ LC3A,B-II+ cells ± SEM. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. P values were calculated by the Mann-Whitney test for unpaired samples (A, B) and one-way ANOVA with the post hoc Tukey multiple comparisons test (D, E).
