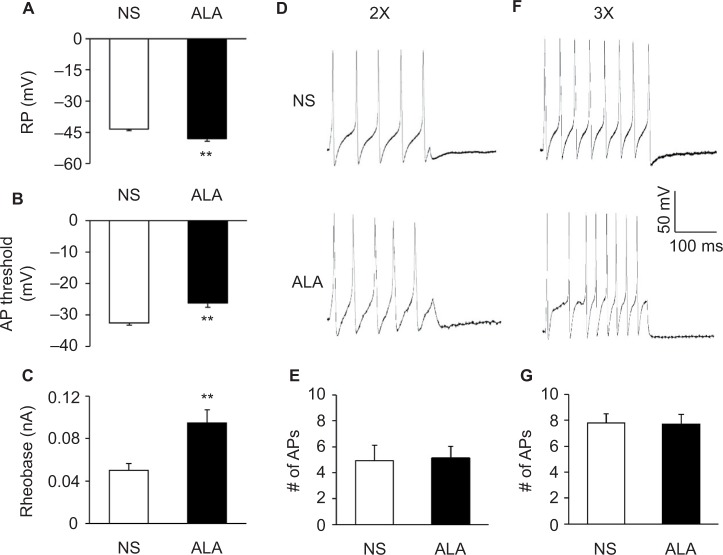
Figure 3.
ALA treatment changed membrane properties of DRG neurons.
Notes: (A) ALA treatment hyperpolarized the RP in DRG neurons (n=24 for each group, **p<0.01, compared with NS, Mann–Whitney test). (B) ALA treatment remarkably depolarized AP threshold (n=24 for each group, **p<0.01, compared with NS, two-sample t-test). (C) ALA treatment resulted in a marked increase of rheobase (n=24 for each group, **p<0.01, compared with NS, Mann–Whitney test). (D, F) Examples of AP trances evoked by 2× (left) and 3× (right) rheobase current stimulation of DRG neurons from NS- (top) and ALA-treatment rats (bottom). (E, G) Bar graphs showed that ALA treatment did not change frequencies of APs evoked by 2 times (2×) and 3 times (3×) rheobase current stimulation (n=24 for each group, p>0.05, Mann–Whitney test and two-sample t-test).
Abbreviations: ALA, α-lipoic acid; AP, action potential; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; NS, normal saline; RP, resting membrane potential.