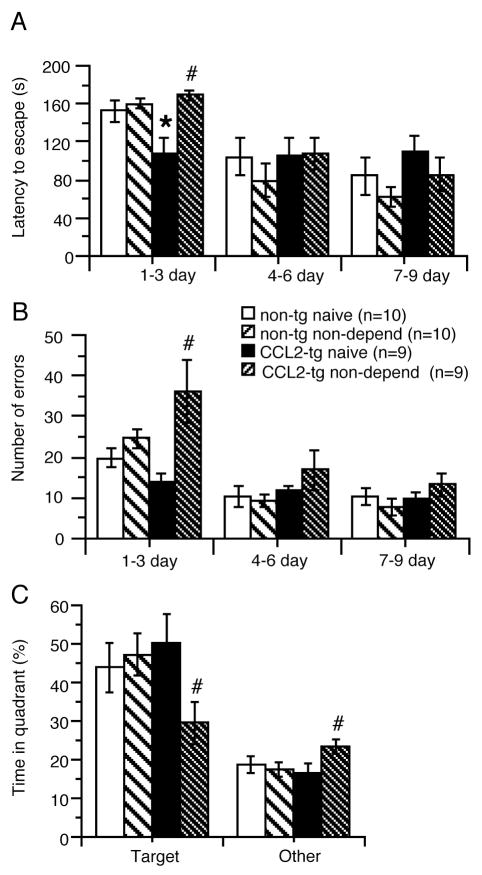
Figure 2.
Alcohol-induced impairments in spatial learning in non-dependent CCL2-tg mice. (A–C) Non-dependent CCL2-tg mice subjected to the 2BC drinking paradigm showed impairments in spatial learning and memory in the Barnes maze test compared with the alcohol naïve CCL2-tg mice. Data were averaged over 3 day periods. During the first time period (1–3 d) non-dependent CCL2-tg mice had increased latency (A), errors to escape (B) and spent less time in the target quadrant (C). Non-dependent and alcohol naïve non-tg mice exposed to the same paradigms did not show impairments. *significant genotypic difference for the same group. # significant group difference for the same genotype.