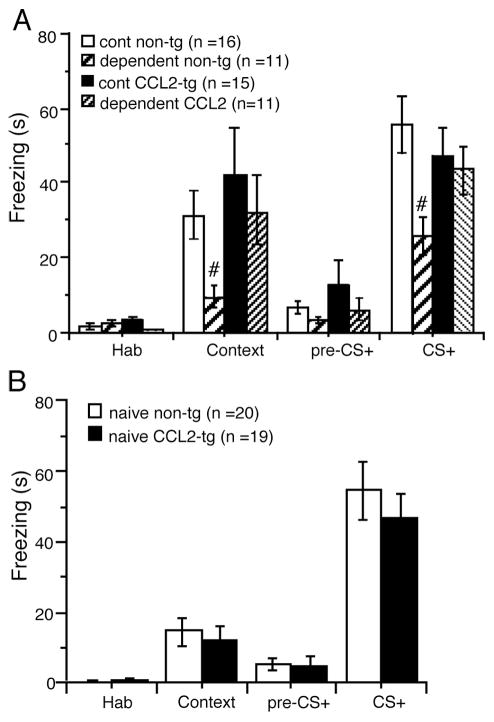
Figure 4.
Dependent CCL2-tg mice were resistant to alcohol-induced impairment in associative learning. Mice made alcohol dependent by the CIE/2BC paradigm were assessed for impairment in associative learning in the cued and contextual fear conditioning task. Learning was assessed by measurement of freezing behavior. Freezing was significantly reduced In the dependent non-tg mice relative to control non-tg mice during both the context test and condition stimulus (CS+) test. There was no significant effect on freezing in either test for the dependent CCL2-tg mice relative to control CCL2-tg mice. #significant group difference for the same genotype.