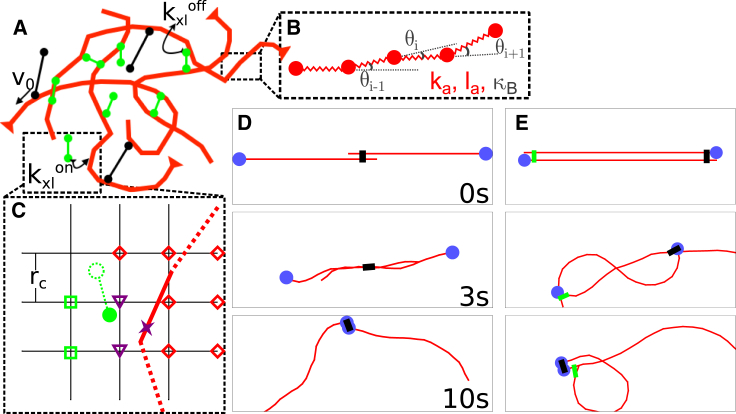
Figure 1.
Overview of the model. See Materials and Methods for details. (A) Shown here is a schematic of a configuration of the model. Filaments are red, cross-linkers are green, and motors are black. (B) Shown here is an expanded view of the actin filament representation: a chain of beads connected by springs with spring constant ka, rest length la, and bending modulus κB, as detailed in Filaments. (C) Shown here is the process by which a cross-linker finds a filament to bind, as detailed in Cross-linkers. The solid red link is indexed to the grid points marked with either red diamonds or purple triangles, and the solid green motor head (circle) searches the grid points marked with either green squares or purple triangles for links to bind. The cross-linker head then stochastically binds to the nearest spot on the filament (see Supporting Materials and Methods and Fig. S1A) here marked with a purple x. (D) Shown here are successive images of two antiparallel 10 μm filaments (barbed ends marked by blue circles) interacting with one motor at the center. The motor binds to both filaments and slides them past each other. (E) This is similar to (D) but with a cross-linker that pins the top filament’s pointed end to the bottom filament’s barbed end. The motor, bound to both, walks toward the barbed end of the bottom filament and buckles the top filament. To see this figure in color, go online.