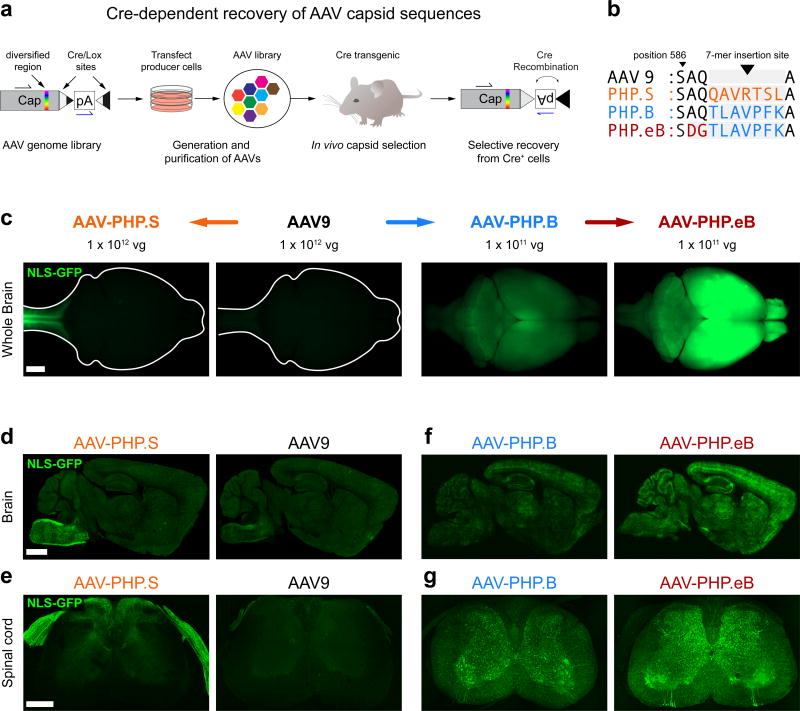
Figure 1. Engineered AAV capsids for efficient transduction across the peripheral and central nervous systems.
(a) Schematic of the CREATE selection method. (b) The amino acid (AA) sequences for the 7-mer insertions and flanking sequences for AAV-PHP.S, .B and .eB; the 7-mer and adjacent substitutions are highlighted in colored text. (c–g) ssAAV-CAG-NLS-GFP was packaged into the indicated capsid and intravenously injected into adult mice at 1 × 1012 vg/mouse (AAV9 and AAV-PHP.S; c–e) or 1 × 1011 vg/mouse (AAV-PHP.B and AAV-PHP.eB; c, f, and g). (c) Representative whole-brain fluorescence images after three weeks of expression. (d–g) Representative confocal images of native GFP fluorescence from sagittal brain sections (d and f) and transverse spinal cord sections (e and g) are shown for the indicated capsids. For (d–g), all imaging and display conditions are matched across panel pairs to allow for comparisons. Panels (d) and (f) are 40 µm maximum intensity projections (MIPs) and panels (e) and (g) are 300 µm MIPs. Scale bars for (c–e) are 1 mm.