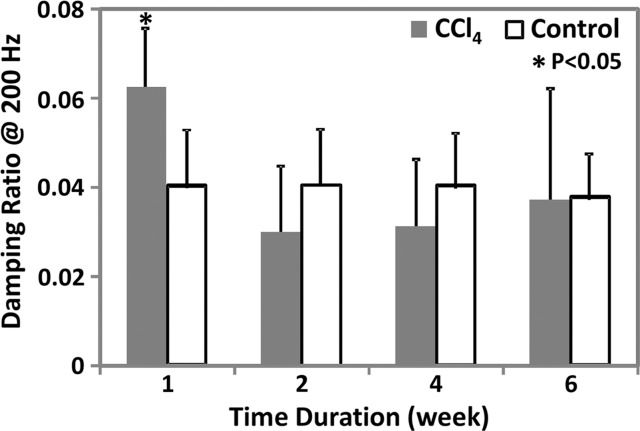
Figure 3c:
MR elastography results and histologic analyses in the CCl4 mouse model. (a) Chart shows necroinflammation and fibrosis extent in the livers of mice with disease and CCl4 administration. All control animals had normal histologic findings. (b, c) MR elastography results of liver stiffness (b) and damping ratio (c) at 200 Hz. Paired t tests were performed to compare CCl4 mice and age-matched control animals at 1, 2, 4, and 6 weeks of administration. (The number of animals was 3:3 for each comparison.) Shear stiffness (b) and damping ratio (c) showed that the liver stiffness increased gradually with the CCl4 exposure time and could be used to detect significant fibrosis at weeks 4 and 6. Early liver injury could be distinguished with only the significantly increased damping ratio in the treatment group.