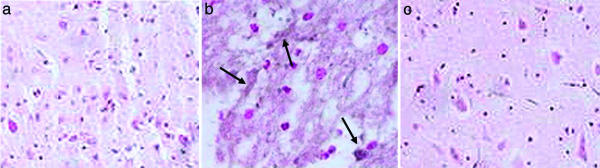
Fig. 4.
UA administration prevents nitrotyrosine formation after SCI. CD1 mice were subjected to SCI and treated with UA or saline as detailed in the legend to Fig. 2. Spinal cord tissues were collected 24 h after trauma and fixed in paraformaldehyde. Nitrotyrosine, a marker of peroxynitrite reactivity, was assessed in paraffin-embedded sections of spinal cord tissue from sham-operated (a), saline-treated (b; arrows indicate accumulations of nitrotyrosine), and UA-treated (c) SCI mice by immunohistochemistry as described in Materials and Methods and photographed (×200).