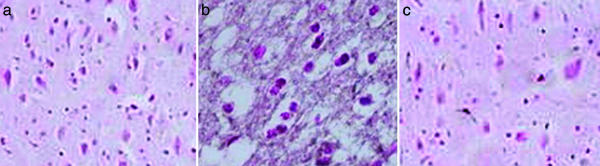
Fig. 5.
UA administration reduces PARP activation after SCI. CD1 mice were subjected to compression-induced SCI and treated with UA or saline as described in the legend to Fig. 2. Spinal cord tissues were collected 24 h after trauma and fixed in paraformaldehyde. Immunohistochemical analysis of poly(ADP-ribose) as a marker of PARP activity was performed in paraffin-embedded sections from the spinal cord tissues of sham-operated (a), saline-treated (b), and UA-treated (c) SCI mice as described in Materials and Methods and photographed (×200).