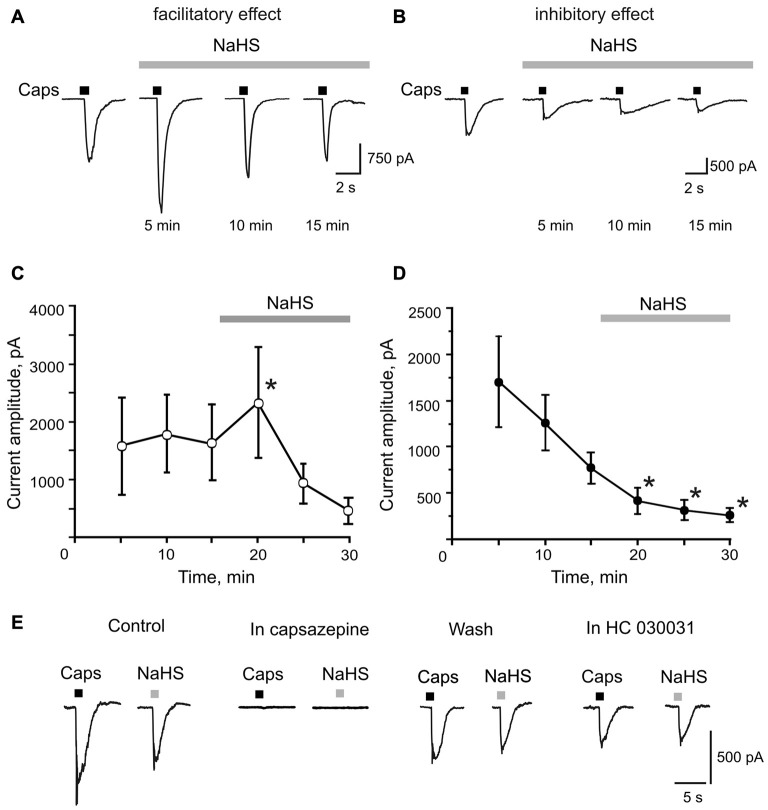
Figure 2.
Facilitatory and inhibitory effects of NaHS on capsaicin induced currents in rat TG neurons. (A,B) Representative traces of capsaicin evoked currents (Caps, 1 μM, 2 s, short bars above traces) in control and during bath application of 100 μM NaHS for 15 min (solid bar above traces). Capsaicin was applied at an interval of 5 min to prevent desensitization of TRPV1 receptors. (C,D) Average amplitude of TRPV1 currents in control (three subsequent capsaicin application) and during NaHS application (solid bars above traces). Notice the increase of mean amplitude of TRPV1 currents after 5 min of NaHS perfusion in (C) and the constant decrease of capsaicin evoked currents in (D). (E) Representative traces of currents evoked by focal application of 1 μM capsaicin (Caps, 2 s) and 100 μM NaHS (2 s) in control and after inhibition of TRPV1 receptors by capsazepine (10 μM); after washout and after inhibition of TRPA1 receptors by HC 030031 (50 μM). Notice that NaHS and capsaicin evoked currents were completely abolished by capsazepine. *p < 0.05 compared to the third application of capsaicin in control.