Figure 9.
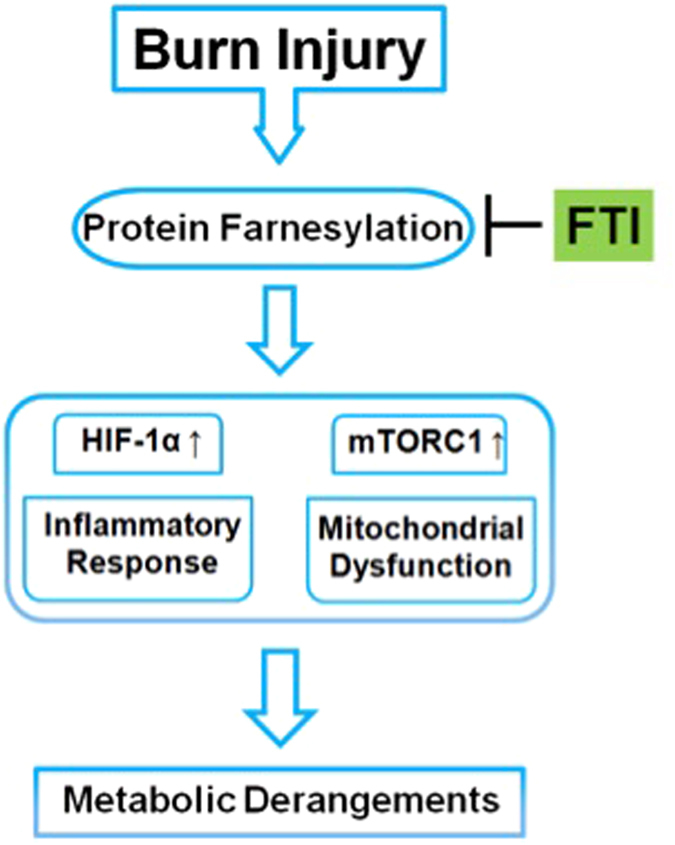
Schematic presentation of the proposed model: Role of protein farnesylation in burn-induced metabolic derangements. Our data indicate that protein farnesylation causes and/or exacerbates activation of the HIF-1α pathway and mTORC1, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ER stress, all of which contribute in concert to burn-induced muscle metabolic derangements, including insulin resistance and increases in lactate production and protein breakdown. Farnesyltransferase (FTase) inhibitor (FTI) prevents burn-induced metabolic derangements by inhibiting or mitigating the impact of burn injury on HIF-1α, mTORC1, mitochondria, and ER stress in mouse skeletal muscle.
