Fig. 7.
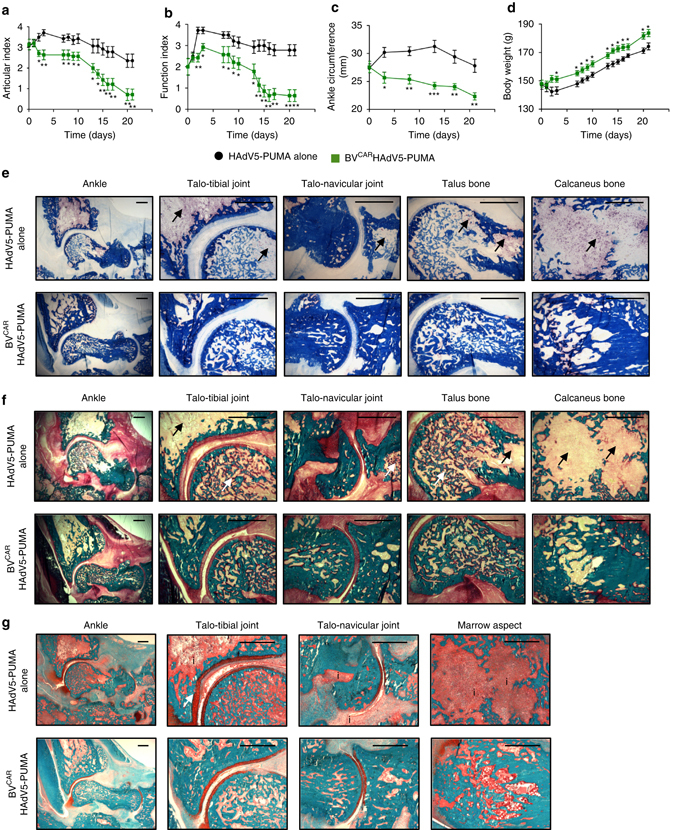
Long term in vivo and in vitro analysis of PUMA gene transfer. Rat ankle joints were injected with HAdV5-PUMA alone, or BVCARHAdV5-PUMA at a vector dose of 109 HAdV5-PUMA per joint, after the onset of arthritis at day 14. The parameters monitored over a period of 21 days were the a ankle articular index, b loss of function index, c ankle circumferences and d body weights. Histology was performed on undecalcified samples with various staining. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining provided red colour in multinucleated osteoclasts on the bone counter-stained with Anilin blue e. Compared to HAdV5-PUMA group, TRAP+ osteoclast staining with the TRAP was reduced at several sites of the ankle area, including distal tibia, talus, calcaneus and navicular bones in the HAdV5-PUMA group. Arrows showed important TRAP+ osteoclast concentration in the bones. In the same sites, the bone matrix was stained with Goldner trichrome staining f. Mineralized matrix was stained in green, while non-mineralized matrix was stained in red and the marrow in yellow. Arrows showed loss of bone mineral. More mineralized trabeculae and less non-mineralized areas were observed in the bones of the BVCARHAdV5-PUMA group in comparison with the HAdV5-PUMA group f. Then, Safranin O–Fast green staining was performed with bone tissue staining in turquoise and cartilage staining in red g. Compared to HAdV5-PUMA, cartilage thickness and its regularity were preserved in the BVCARHAdV5-PUMA group. Arrows indicated the loss of mineral in the bones. Inflammatory infiltrate (indicated by the ‘i’) was importantly diminished in the HAdV5-PUMA group and the bone cavity conserved its histological integrity. Scale bar, 500 µm
