Figure 1.
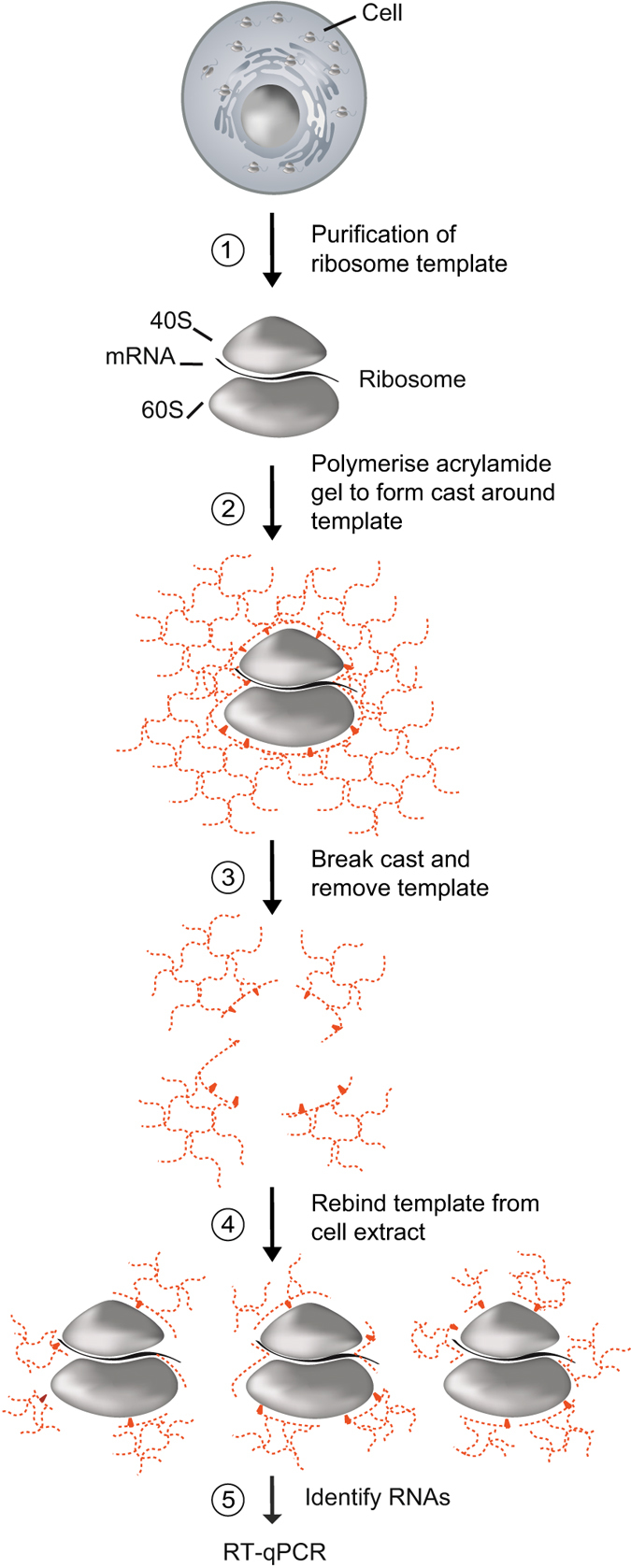
Schematic overview of R-MIP preparation. First, ribosomes are isolated from HeLa cell cytoplasmic extract using a sucrose cushion. Second, the ribosome template is combined with a mixture of acrylamide (AA) and N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAm) monomers, and polymerisation is induced under gaseous nitrogen upon addition of the initiator ammonium persulfate (APS) and the catalyst N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED). Third, the hydrogel is granulated by passing through a sieve mesh, and the ribosome template is removed from the MIP. This results in a slurry of heterogeneous PAA fragments, with cavities possessing the potential to recognise more template, based both upon three dimensional structure and direct interactions between the template and chemical groups on the surfaces of the cavities. Fourth, MIPs are combined with cellular extracts to capture ribosomes and associated mRNAs. Fifth, ribosome-associated mRNAs are isolated from the MIP for further analysis, such as reverse transcription (RT)-quantitative PCR (qPCR).
